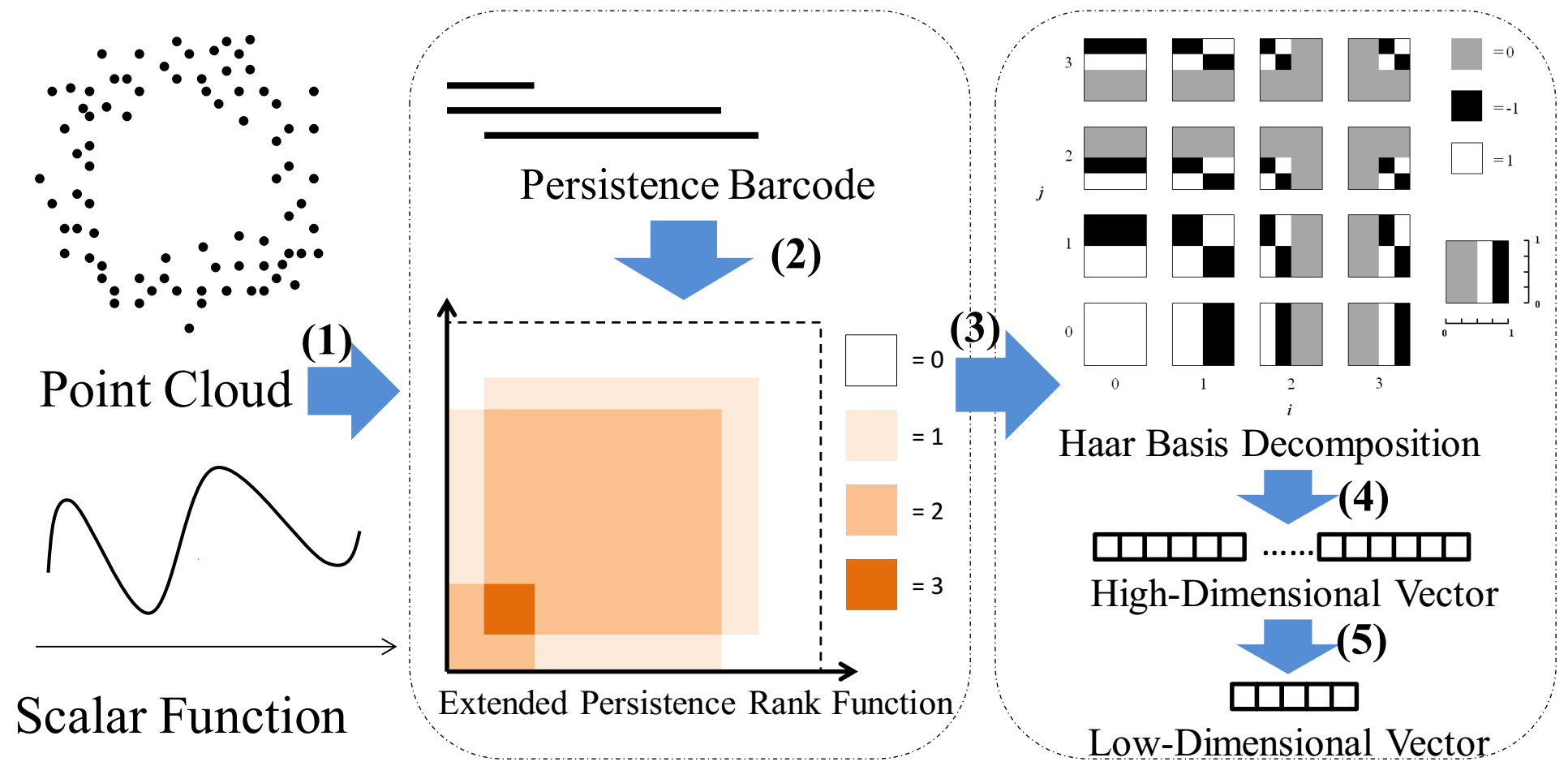
Vectorization of persistence barcode with applications in pattern classification of porous structures pdf
Zhetong Dong, Chuanfeng Hu, Chi Zhou, Hongwei Lina
Accepted by SMI'2020
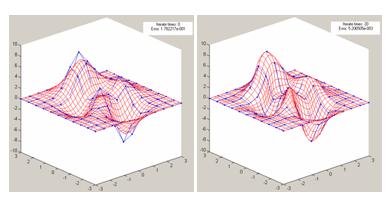
Persistence barcode is a topological summary for persistent homology to exhibit topological features with different persistence. Persistence rank function (PRF), derived from persistence barcode, organizes persistence Betti numbers in the form of an integervalued function. To obtain topological patterns of objects such as point clouds represented by finite-dimensional vectors for machine learning classification tasks, the vectorizing representations of barcodes is generated via decomposing PRF on a system of Haar basis. Theoretically, the generated vectorizing representation is proved to have 1-Wasserstein stability. In practice, to reduce training time and achieve better results, a technique of dimensionality reduction through out-of-sample mapping in supervised manifold learning is used to generate a low-dimensional vector. Experiments demonstrate that the representation is effective for capturing the topological patterns of data sets. Moreover, the classification of porous structures has become an essential problem in the fields such as material science in recent decades. The proposed method is successfully applied to distinguish porous structures on a novel data set of porous models.
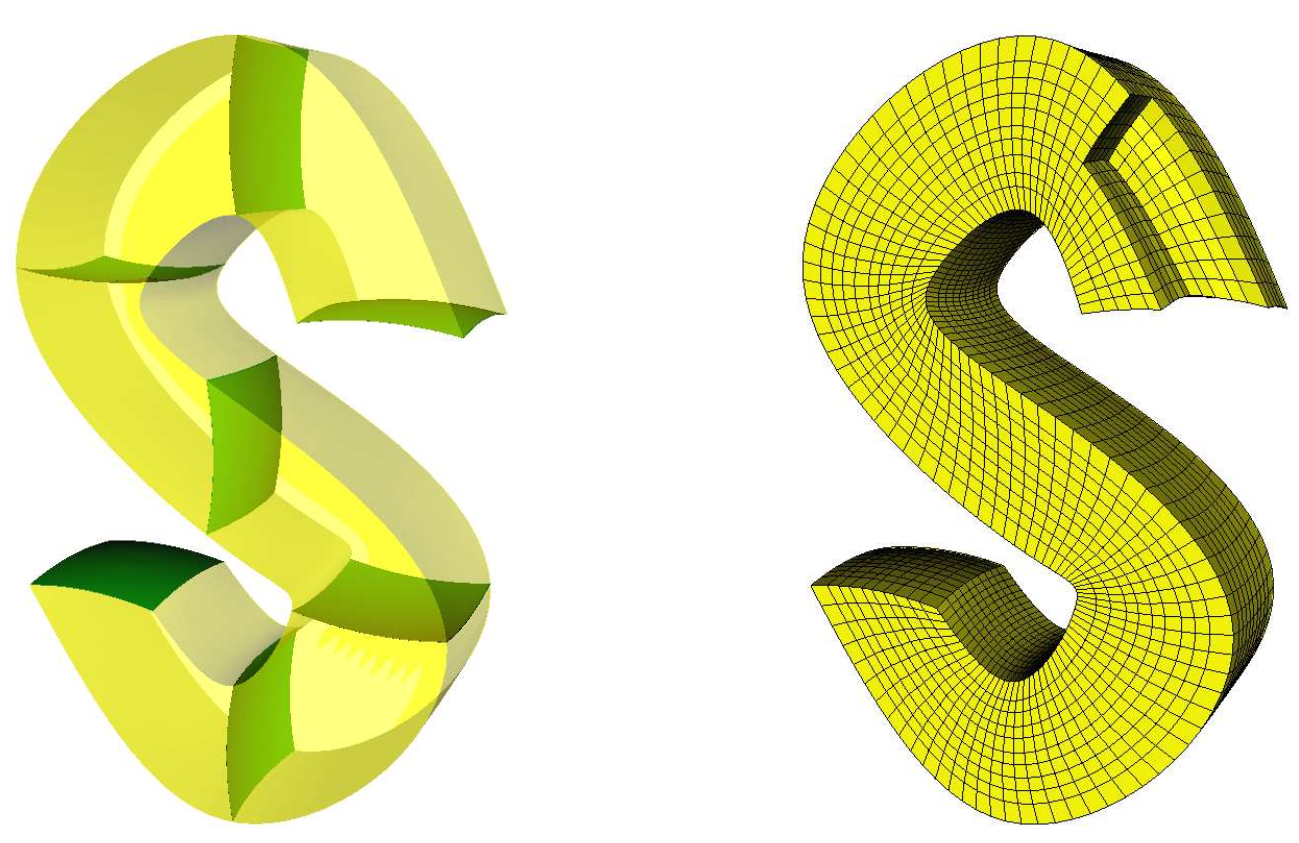
Curve guided T-spline skinning for surface and solid generation pdf
Chuanfeng Hu, Jiaming Ai, Hongwei Lin
Computers & Graphics, in press
Skinning is an essential technology in geometric modeling. Unlike non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) skinning, T-spline skinning does not require knot compatibility of the given cross-sections, and avoids superfluous of control points. In this study, we present a curve guided T-spline (CGTS) skinning method for surface and solid generation of high quality, which interpolates the given cross-sections. Guiding curves and least squares progressive and iterative approximation (LSPIA) method are involved in the CGTS skinning. Specifically, the guiding curves provide a visually pleasing shape for the skinned surface and solid, and the LSPIA method simplifies the iterative procedure, ensures the fitting accuracy, and shape preservation. On one hand, the CGTS surface skinning generates a visually pleasing and fairing skinned T-spline surface, which avoids the wiggle and crease problems. On the other hand, the CGTS solid skinning with optimization generates a trivariate T-spline solid with high quality. To meet the requirement of iso-geometric analysis (IGA) for the skinned T-spline solid, an optimization approach is employed in the solid skinning to improve the quality of the skinned T-spline solid. Finally, the experimental examples presented in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the CGTS skinning method.
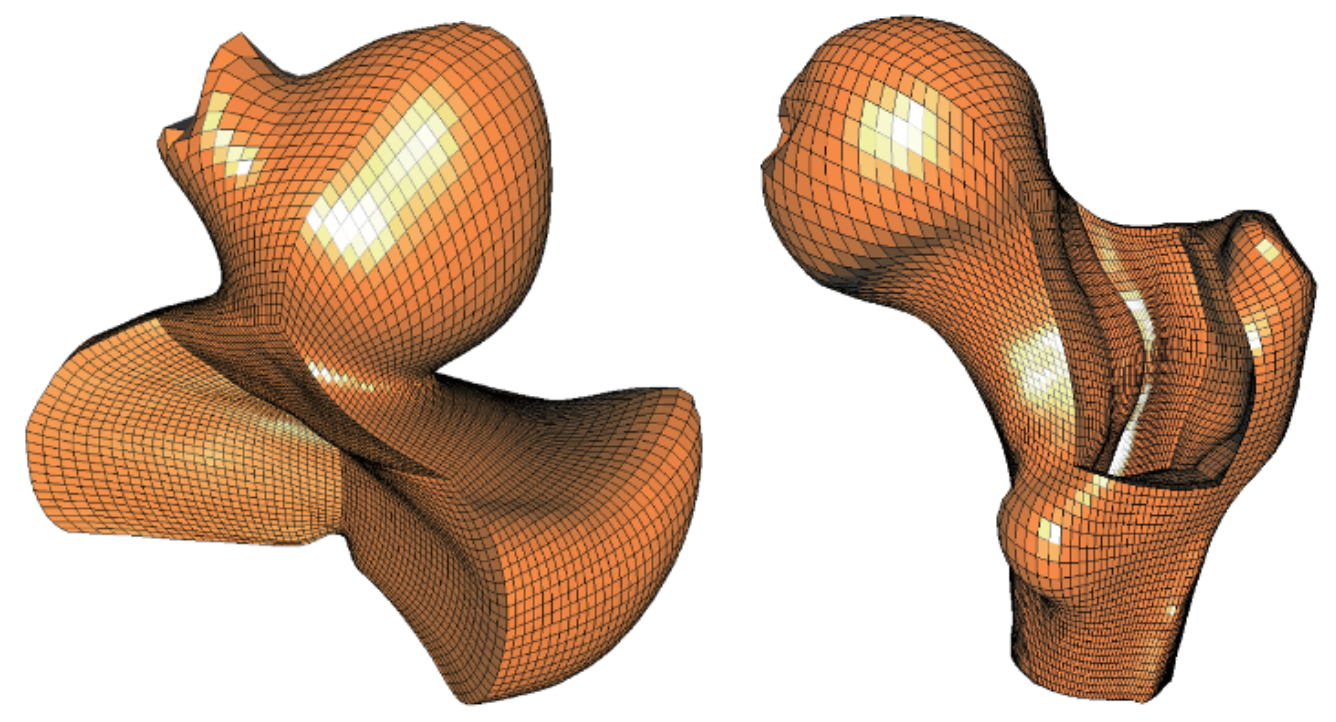
Gregory Solid Construction for Polyhedral Volume Parameterization by Sparse Optimization pdf
Applied Mathematics, A Journal of Chinese University, 34(3), 340-355, 2019
Chuanfeng Hu, Hongwei Lin
In isogeometric analysis, it is frequently required to handle the geometric models enclosed by four-sided or non-four-sided boundary patches, such as trimmed surfaces. In this paper, we develop a Gregory solid based method to parameterize those models. First, we extend the Gregory patch representation to the trivariate Gregory solid representation. Second, the trivariate Gregory solid representation is employed to interpolate the boundary patches of a geometric model, thus generating the polyhedral volume parametrization. To improve the regularity of the polyhedral volume parametrization, we formulate the construction of the trivariate Gregory solid as a sparse optimization problem, where the optimization objective function is a linear combination of some terms, including a sparse term aiming to reduce the negative Jacobian area of the Gregory solid. Then, the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) is used to solve the sparse optimization problem. Lots of experimental examples illustrated in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the developed method.
A dimensional reduction guiding deep learning architecture for 3D shape retrieval. pdf
Computers & Graphics, 81, 82-91, 2019
Zihao Wang, Hongwei Lin, Xiaofeng Yu, Yusuf Fatihu Hamza
The state-of-the-art shape descriptors are usually lengthy for gaining high retrieval precision. With the rapidly growing number of 3-dimensional models, the retrieval speed becomes a prominent problem in shape retrieval. In this paper, by exploiting the capabilities of the dimensionality reduction methods and the deep convolutional residual network (ResNet), we developed a method for extracting short shape descriptors (with just 2 real numbers, named 2-descriptors) from lengthy descriptors, while keeping or even improving the retrieval precision of the original lengthy descriptors. Specifically, an attraction and repulsion model is devised to strengthen the direct dimensionality reduction results. In this way, the dimensionality reduction results turn into desirable labels for the ResNet. Moreover, to extract the 2-descriptors using ResNet, we transformed it as a classification problem. For this purpose, the range of each component of the dimensionality reduction results (including two components in total) is uniformly divided into n intervals corresponding to n classes. Experiments on 3D shape retrieval show that our method not only accelerates the retrieval speed greatly but also improves the retrieval precisions of the original shape descriptors.
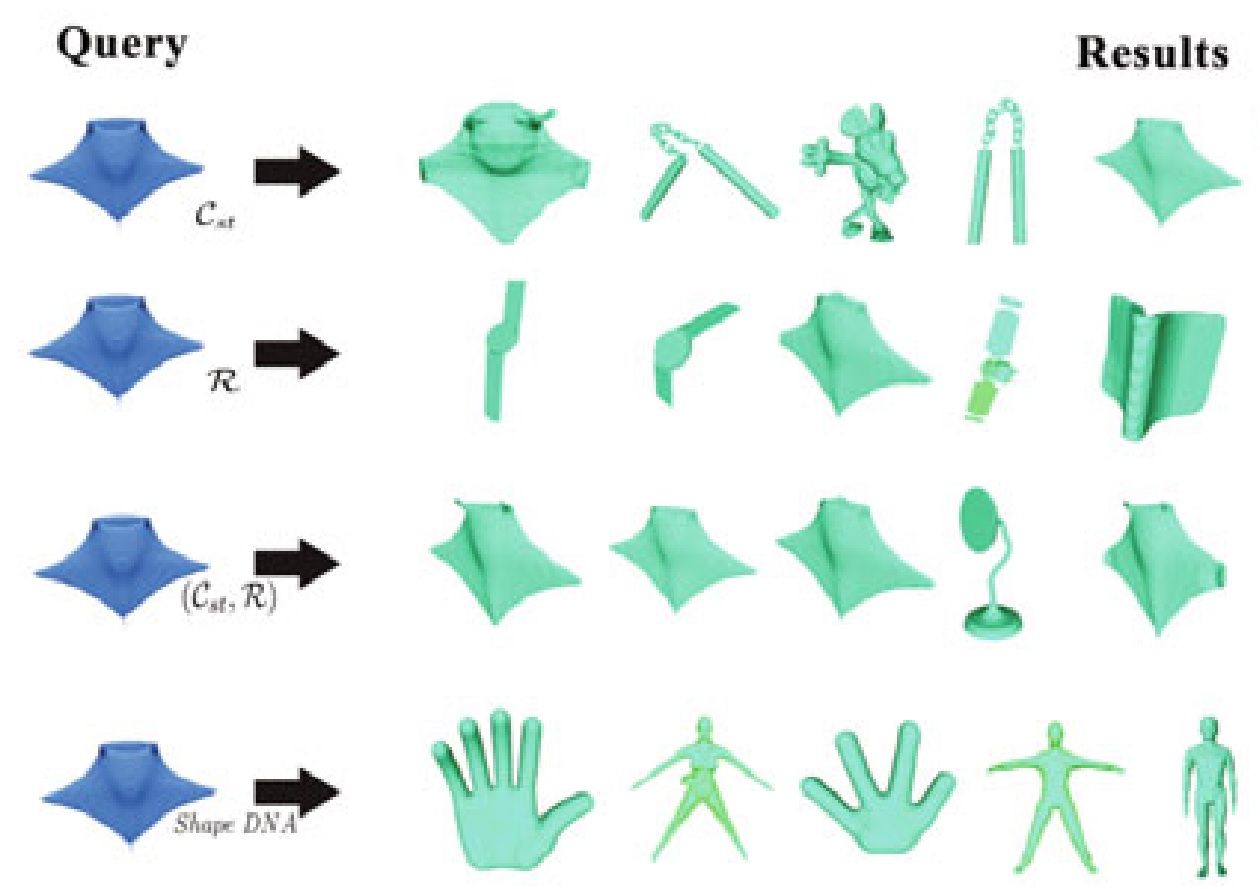
Data driven composite shape descriptor design for shape retrieval with a VoR-Tree. pdf
Applied Mathematics, A Journal of Chinese University, 33(1), 88-106, 2018
Zihao Wang, Hongwei Lin, Chenkai Xu
We develop a data driven method (probability model) to construct a composite shape descriptor by combining a pair of scale-based shape descriptors. The selection of a pair of scale-based shape descriptors is modeled as the computation of the union of two events, i.e., retrieving similar shapes by using a single scale-based shape descriptor. The pair of scale-based shape descriptors with the highest probability forms the composite shape descriptor. Given a shape database, the composite shape descriptors for the shapes constitute a planar point set. A VoR-Tree of the planar point set is then used as an indexing structure for efficient query operation. Experiments and comparisons show the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed composite shape descriptor.
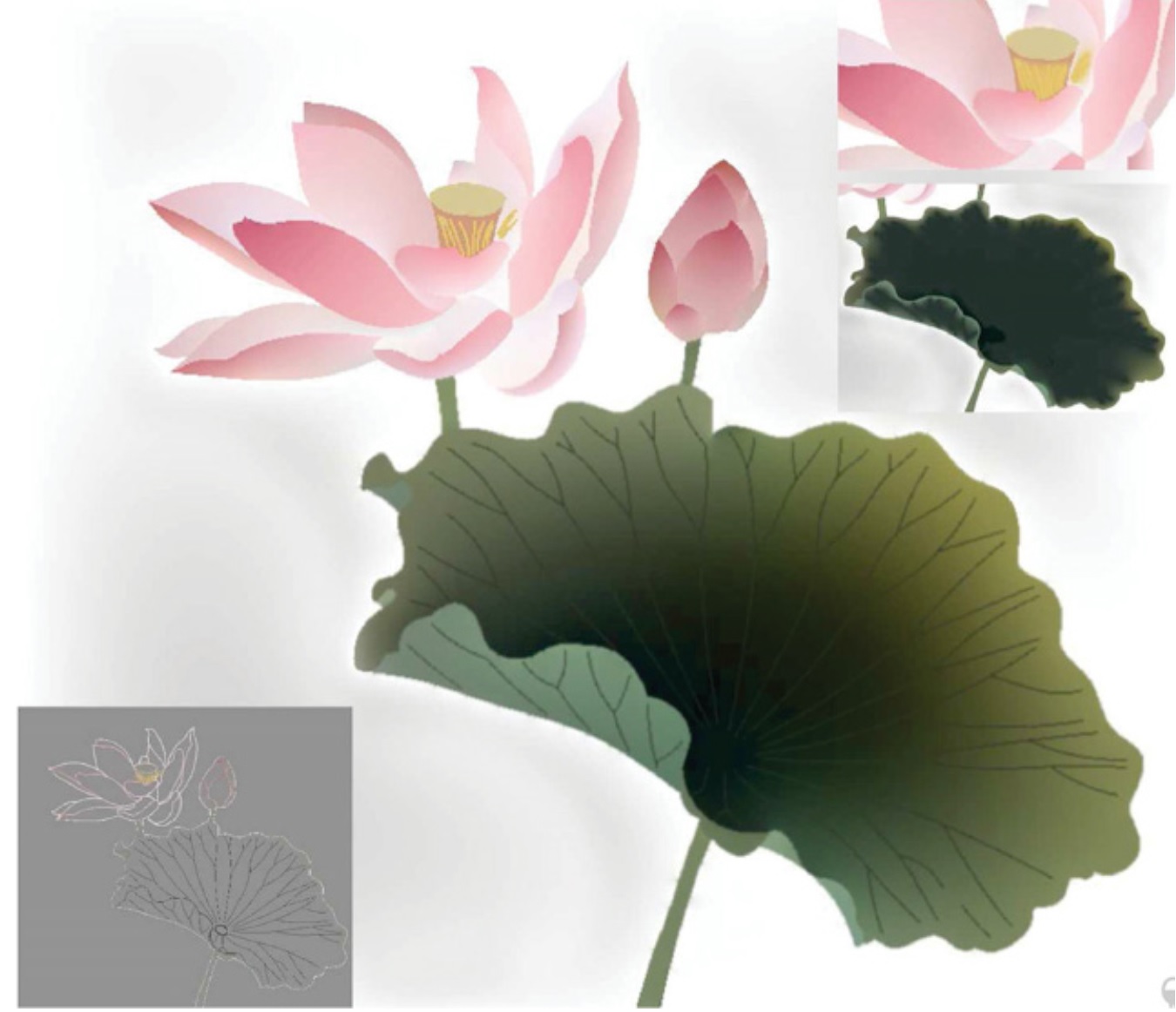

Diffusion curves with diffusion coefficients. pdf
Computational Visual Media, 4(2), 149-160, 2018
Hongwei Lin, Jingning Zhang, Chenkai Xu
Diffusion curves can be used to generate vector graphics images with smooth variation by solving Poisson equations. However, using the classical diffusion curve model, it is difficult to ensure that the generated diffusion image satisfies desired constraints. In this paper, we develop a model for producing a diffusion image by solving a diffusion equation with diffusion coefficients, in which color layers and coefficient layers are introduced to facilitate the generation of the diffusion image. Doing so allows us to impose various constraints on the diffusion image, such as diffusion strength, diffusion direction, diffusion points, etc., in a unified computational framework. Various examples are presented in this paper to illustrate the capabilities of our model.
Survey on geometric iterative methods and their applications. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 95, 40-51, 2018
Hongwei Lin, Takashi Maekawa, Chongyang Deng
Geometric iterative methods (GIM), including the progressive–iterative approximation (PIA) and the geometric interpolation/approximation method, are a class of iterative methods for fitting curves and surfaces with clear geometric meanings. In this paper, we provide an overview of the interpolatory and approximate geometric iteration methods, present the local properties and accelerating techniques, and show their convergence. Moreover, because it is easy to integrate geometric constraints in the iterative procedure, GIM has been widely applied in geometric design and related areas. We survey the successful applications of geometric iterative methods, including applications in geometric design, data fitting, reverse engineering, mesh and NURBS solid generation.
The Convergence of Least-Squares Progressive Iterative Approximation for Singular Least-Squares Fitting System. pdf
Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, in press, 2017
Hongwei Lin, Qi Cao, Xiaoting Zhang
Data fitting is an extensively employed modeling tool in geometric design. With the advent of the big data era, the data sets to be fitted are made larger and larger, leading to more and more leastsquares fitting systems with singular coefficient matrices. LSPIA (least-squares progressive iterative approximation) is an efficient iterative method for the least-squares fitting. However, the convergence of LSPIA for the singular least-squares fitting systems remains as an open problem. In this paper, we showed that LSPIA for the singular least-squares fitting systems is convergent. Moreover, in a special case, LSPIA converges to the Moore-Penrose (M-P) pseudo-inverse solution to the least-squares fitting result of the data set. This property makes LSPIA, an iterative method with clear geometric meanings, robust in geometric modeling applications. In addition, we discussed some implementation detail of LSPIA, and presented an example to validate the convergence of LSPIA for the singular least-squares fitting systems
Trivariate B-spline Solid Construction by Pillow Operation and Geometric Iterative Fitting. pdf supporting information
SCIENCE CHINA Information Science, in press, 2017
Hongwei Lin, Hao Huang, Chuanfeng Hu
The advent of isogeometric analysis has prompted a need for methods to generate Trivariate B-spline Solids (TBS) with positive Jacobian. However, it is difficult to guarantee a positive Jacobian of a TBS since the geometric pre-condition for ensuring the positive Jacobian is very complicated. In this paper, we propose a method for generating TBSs with guaranteed positive Jacobian. For the study, we used a tetrahedral (tet) mesh model and segmented it into sub-volumes using the pillow operation. Then, to reduce the difficulty in ensuring a positive Jacobian, we separately fitted the boundary curves and surfaces and the sub-volumes using a geometric iterative fitting algorithm. Finally, the smoothness between adjacent TBSs is improved. The experimental examples presented in this paper demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the developed algorithm.
Isogeometric Least-squares Collocation Method with Consistency and Convergence Analysis. pdf
TR-ZJU-GDC-2017-001, arXiv:1601.07244v2
Hongwei Lin, Yunyang Xiong, Xiao Wang, Qianqian Hu
In this paper, we present the isogeometric least-squares collocation (IGA-L) method, which determines the numerical solution by making the approximate differential operator fit the real differential operator in a least-squares sense. The number of collocation points employed in IGA-L can be larger than that of the unknowns. Theoretical analysis and numerical examples presented in this paper show the superiority of IGA-L over state-of-the-art collocation methods. First, a small increase in the number of collocation points in IGA-L leads to a large improvement in the accuracy of its numerical solution. Second, IGA-L method is more flexible and more stable, because the number of collocation points in IGA-L is variable. Third, IGA-L is convergent in some cases of singular parameterization. Moreover, the consistency and convergence analysis are also developed in this paper.

Computer Simulation and Generation of Moving Sand Pictures. pdf
IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics, in press, 2017
Mohan Zhang, Hongwei Lin, Kang Zhang, Jinhui Yu
Moving sand pictures are interesting devices that can be used to generate an infinite number of unique scenes when repeatedly being flipped over. However, little work has been done on attempting to simulate the process of picture formulation. In this paper, we present an approach capable of generating images in the style of moving sand pictures. Our system defines moving sand pictures in a few steps, such as initialization, segmentation and physical simulation, so that a variety of moving sand pictures including mountain ridges, desert, clouds and even regular patterns can be generated by either automatic or semi-automatic via interaction during initialization and segmentation. Potential applications of our approach range from advertisements, posters, post cards, packaging, to digital arts.
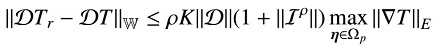
The Convergence Rate and Necessary-and-Sufficient Condition for the Consistency of Isogeometric Collocation Method. pdf
TR-ZJU-GDC-2016-001, arXiv:1607.05807
Hongwei Lin, Yunyang Xiong, Qianqin Hu
Although the isogeometric collocation (IGA-C) method has been successfully utilized in practical applications due to its simplicity and efficiency, only a little theoretical results have been established on the numerical analysis of the IGA-C method. In this paper, we deduce the convergence rate of the consistency of the IGA-C method. Moreover, based on the formula of the convergence rate, the necessary and sufficient condition for the consistency of the IGA-C method is developed. These results advance the numerical analysis of the IGA-C method.
Catmull-Clark细分曲面的正则性. pdf
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 28(9), 1401-1409, 2016
王晶, 蔺宏伟, 王潇, 卢兴江
针对 Catmull-Clark(C-C)细分曲面的正则性进行研究, 得到简单易用的判别 C-C细分曲面正则性的充分条件. 首先给出网格点差分向量的 3 种定义: 前向差分向量, 中心差分向量和后向差分向量; 然后推导出 C-C 细分曲面的差分向量的细分格式; 进一步, 通过特征分析建立了 C-C 细分极限曲面的切向量与初始控制网格差分向量之间的关系; 最后得到判别 C-C 细分极限曲面正则性的一个充分条件. 由于该判别条件表达为初始控制网格差分向量之间的几何关系, 因此这个条件具有明显的几何意义. 实验结果表明, 文中的判别条件易于验证.
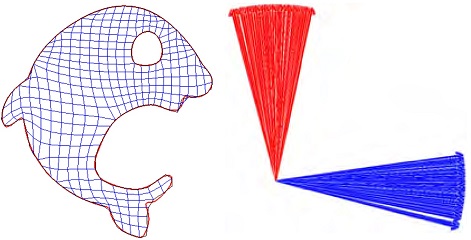
平面n边域上高品质四边网格生成方法. pdf
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 28(11), 1811-1820, 2016
简群, 蔺宏伟, 曹琦, 卢兴江
在有限元分析中, 四边网格比三角网格更难以生成, 特别是在具有复杂形状和拓扑结构的平面域上. 为此, 基于几何迭代算法, 提出一种在形状复杂和高亏格的 n 边平面域上生成高质量四边网格的方法, 并保证生成的四边网格不自交. 该方法以自适应像素化离散技术生成的四边网格作为初始网格, 网格边界迭代拟合至给定的平面区域边界, 其中每次边界迭代后, 通过分层的 Laplace 算子改变内部顶点的位置; 在迭代过程中, 网格顶点的移动都受到限制, 保证生成的网格严格不自交. 最后通过实验验证了文中算法的效率和有效性.

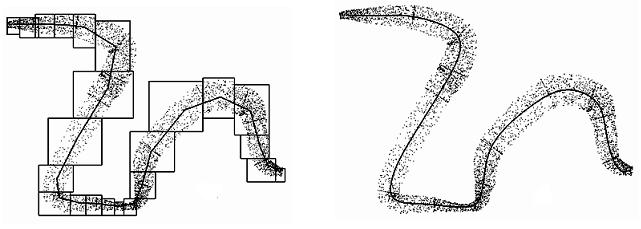
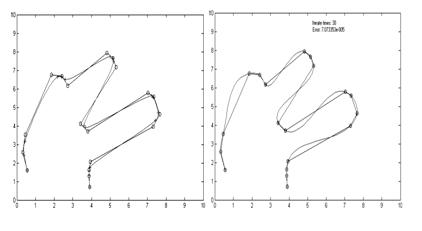
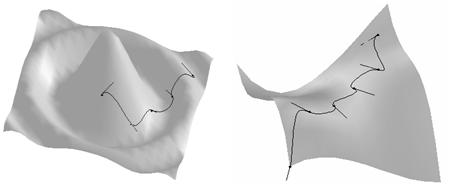
A computational model of topological and geometric recovery for visual curve completion. pdf
Computational Visual Media, 2(4), 329-342
Hongwei Lin, Zihao Wang, Panpan Feng, Xingjiang Lu, and Jinhui Yu
Visual curve completion is a fundamental problem in understanding the principles of the human visual system. This problem is usually divided into two problems: a grouping problem and a shape problem. On one hand, though perception of the visually completed curve is clearly a global task (for example, a human perceives the Kanizsa triangle only when seeing all three black objects), conventional methods for solving the grouping problem are generally based on local Gestalt laws. On the other hand, the shape of the visually completed curve is usually recovered by minimizing shape energy in existing methods. However, not only do these methods lack mechanisms to adjust the shape of the recovered visual curve using perceptual, psychophysical, and neurophysiological knowledge, but it is also difficult to calculate an explicit representation of the visually completed curve. In this paper, we present a systematic computational model for generating a visually completed curve. Firstly, based on recent studies of perception, psychophysics, and neurophysiology, we formulate a grouping procedure based on the human visual system by seeking a minimum Hamiltonian cycle in a graph, solving the grouping problem in a global manner. Secondly, we employ a Bezier curve-based model to represent the visually completed curve. Not only is an explicit representation deduced, but we also present a means to integrate knowledge from related areas, such as perception, psychophysics, and neurophysiology, and so on. The proposed computational model has been validated using many modal and amodal completion examples, and desirable results were obtained.
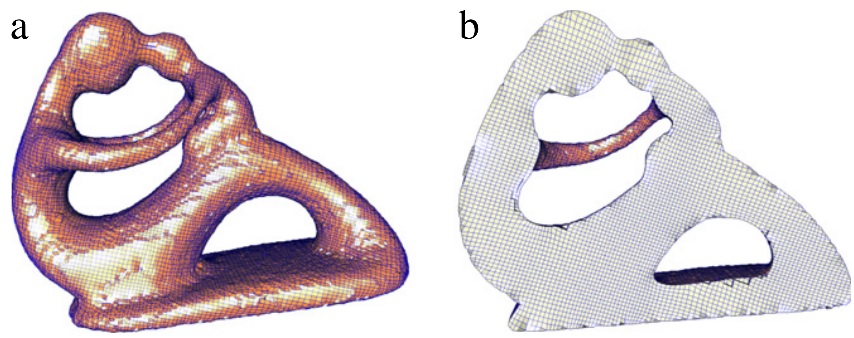
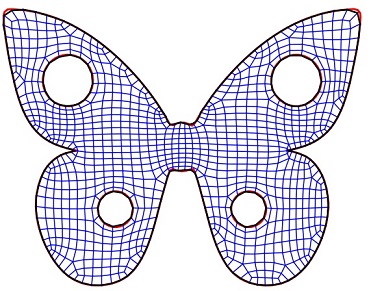
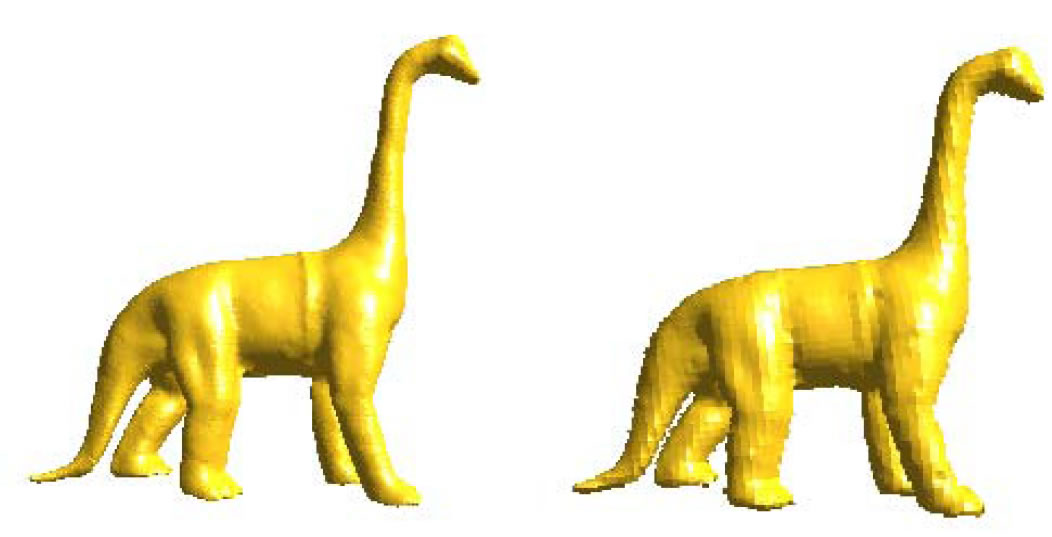
Quality guaranteed all-hex mesh generation by a constrained volume iterative fitting algorithm. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 67-68(107-117), 2015
Hongwei Lin, Sinan Jin, Hongwei Liao, Qun Jian
The hexahedral mesh (hex mesh) is usually preferred to the tetrahedral mesh (tet mesh) in finite element methods for numerical simulation. In finite element analysis, a valid hex mesh requires that the scaled Jacobian value at each mesh vertex is larger than 0. However, the hex mesh produced by lots of
prevailing hex mesh generation methods cannot be guaranteed to be a valid hex mesh. In this paper, we
develop a constrained volume iterative fitting (CVIF) algorithm to fill a given triangular mesh model with
an all-hex volume mesh. Starting from an initial all-hex mesh model, which is generated by voxelizing
the given triangular mesh model, CVIF algorithm fits the boundary mesh of the initial all-hex mesh to
the given triangular mesh model by iteratively adjusting the boundary mesh vertices. In each iteration,
the movements of the boundary mesh vertices are diffused to the inner all-hex mesh vertices. After the
iteration stops, an all-hex volume mesh that fills the given triangular mesh model can be generated. In
the CVIF algorithm, the movement of each all-hex mesh vertex is constrained to ensure that the scaled
Jacobian value at each mesh vertex is larger than 0, etc. Therefore, the all-hex mesh generated by the CVIF algorithm is guaranteed to be a valid all-hex mesh.
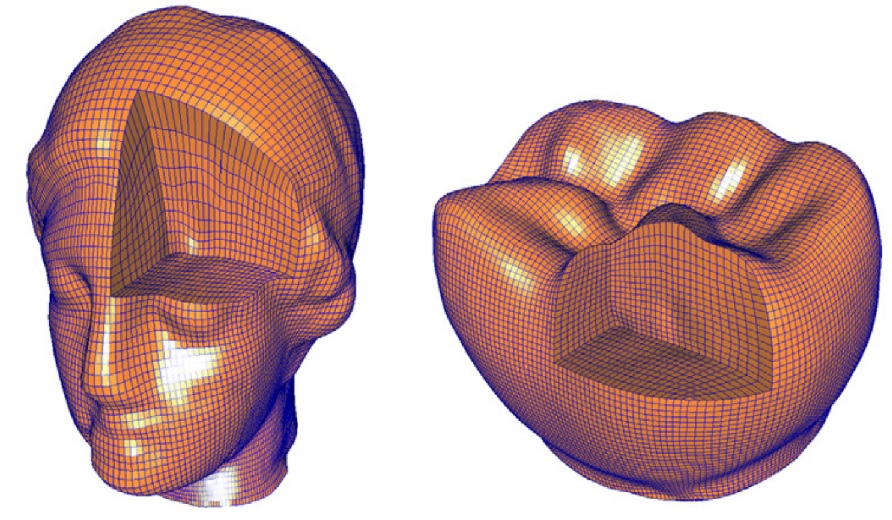
Constructing B-spline solids from tetrahedral meshes for isogeometric analysis. pdf
Computer Aided Geometric Design, 35-36, 109-120, 2015
Hongwei Lin, Sinan Jin, Qianqian Hu, Zhenbao Liu
With the advent of isogeometric analysis, the modeling of spline solids became an
important topic. In this paper, we present a discrete volume parameterization method for
tetrahedral (tet) mesh models and an iterative fitting algorithm with a B-spline solid. The
discrete volume parameterization method maps the vertices of a tet mesh into a parameter
domain by solving a system of linear equations. Each equation is explicitly constructed
for an inner vertex in terms of the geometric information adjacent to the inner vertex.
Moreover, we show the validity of the parameterization system of linear equations thus
constructed. Next, because the number of tet mesh vertices is usually very large, we
develop an iterative algorithm for fitting a tet mesh with a B-spline solid. The iterative algorithm exploits the geometric information of the control hexahedral (hex) mesh and the
local support property of the spline function, so the total amount of computation in each
iteration is unchanged when the number of control hex mesh vertices of the B-spline solid
is increased. Therefore, the iterative fitting algorithm performs very well in incremental
fitting of a tet mesh with a large number of vertices. Finally, four experimental examples
presented in this paper show the efficiency and effectiveness of the developed algorithms.
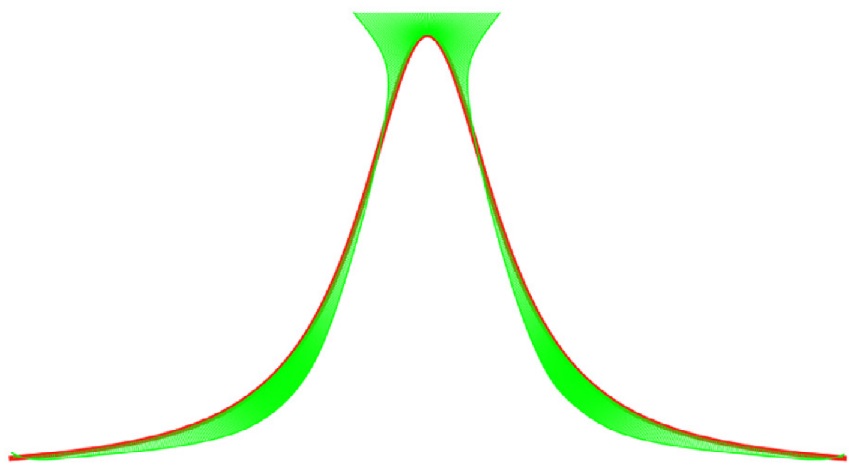
Searching globally optimal parameter sequence for defeating Runge phenomenon by immunity genetic algorithm . pdf
Applied Mathematics and Computation, 264, 85-98, 2015
Hongwei Lin, Linjie Sun
Data interpolation is a fundamental data processing tool in scientific studies and engineering
applications. However, when interpolating data points on an equidistant grid using polynomials, the so-called Runge phenomenon may occur, making polynomial interpolation unreliable.
Although there are some methods proposed to defeat the Runge phenomenon, it is still an
open problem which parameter sequence is the globally optimal for overcoming the Runge
phenomenon. In this paper, we develop an immunity genetic algorithm based method to
solve this problem. Specifically, we first model the Runge-phenomenon-defeating problem
as an optimization in which the objective function is the energy of the parametric curve.
An immunity genetic algorithm is then devised to determine the best IGA parameter sequence, which minimizes the objective function. The resulting parametric curve overcomes
the Runge phenomenon. By performing the proposed immunity genetic searching algorithm
starting with some groups of randomly generated parameter sequences, the resulted parameter sequences closely oscillate around the Chebyshev parameter sequence. Therefore, the
Chebyshev parameter sequence is most likely the globally optimal sequence conquering the
Runge phenomenon.
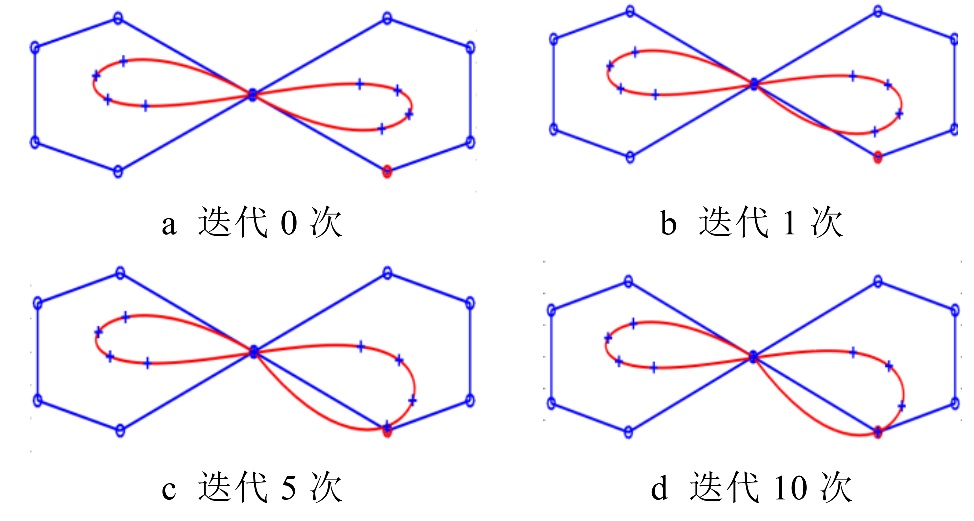
几何迭代法及其应用综述. pdf
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 27(4), 582-589, 2015
蔺宏伟
几何迭代法, 又称渐进迭代逼近(progressive-iterative approximation, PIA), 是一种具有明显几何意义的迭代方法. 它通过不断调整曲线曲面的控制顶点, 生成的极限曲线曲面插值(逼近)给定的数据点集. 文中从理论和应用 2个方面对几何迭代法进行了综述. 在理论方面, 介绍了插值型几何迭代法的迭代格式、收敛性证明、局部性质、加速方法, 以及逼近型几何迭代法的迭代格式和收敛性证明等. 进而,展示了几何迭代法在几个方面的成功应用, 包括自适应数据拟合、大规模数据拟合、对称曲面拟合, 以及插值给定位置﹑切矢量和曲率矢量的曲线迭代生成, 有质量保证的四边网格和六面体网格生成, 三变量 B-spline .
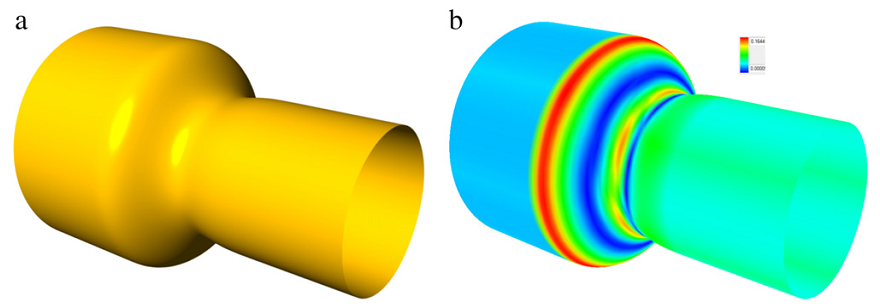
Semi-structured B-spline for blending two B-spline surfaces. pdf
Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 68, 706-718, 2014.10
Hongwei Lin, Yunyang xiong, Hongwei Liao
Surface blending is a useful operation in geometric design for rounding sharp edges or corners. Meanwhile, NURBS has already become the de facto industrial standard in existing CAD/CAM systems. Therefore, it is required to study how to blend two B-spline surfaces. However, two arbitrary B-spline surfaces (called base surfaces) are hard to be blended with a B-spline surface (called blending surface) because the knot vectors of the two base surfaces are usually mismatched. In this paper, we proposed a curve-based spline representation, i.e., the semi-structured B-spline surface, which is generated by skinning a series of B-spline curves with different knot vectors. By assigning suitable knot vectors to the head and tail skinned curves, the semi-structured B-spline surface can blend two B-spline surfaces smoothly without disturbing them at all. We formulated the B-spline surface blending problem as an optimization problem with continuity constraints, and the continuity between the base and blending surfaces can reach G2 or C2. Examples illustrated in this paper validate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method.
Affine Arithmetic Based B-spline Surface Intersection with GPU Acceleration. pdf
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 20(2), 172-181, 2014.2
Hongwei Lin, Yang Qin, Hongwei Liao, Yunyang Xiong.
Because the B-spline surface intersection is a fundamental operation in geometric design software, it is important to make the surface intersection operation robust and efficient. As is well known, affine arithmetic is robust for calculating the surface intersection because it is able to not only find every branch of the intersection, but also deal with some singular cases, such as surface tangency. However, the classical affine arithmetic is defined only for the globally supported polynomials, and its computation is very time consuming, thus hampering its usefulness in practical applications, especially in geometric design. In this paper, we extend affine arithmetic to calculate the range of recursively and locally defined B-spline basis functions, and we accelerate the affine arithmetic-based surface intersection algorithm by using a GPU. Moreover, we develop efficient methods to thin the strip-shaped intersection regions produced by the affine arithmetic-based intersection algorithm, calculate the intersection points, and further improve their accuracy. The many examples presented in this paper demonstrate the robustness and efficiency of this method.
Progressive and iterative approximation for least squares B-spline curve and surface fitting. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 47, 32-44, 2014.2.
Chongyang Deng, Hongwei Lin.
The progressive and iterative approximation (PIA) method is an efficient and intuitive method for data fitting. However, in the classical PIA method, the number of the control points is equal to that of the data points. It is not feasible when the number of data points is very large. In this paper, we develop a new progressive and iterative approximation for least square fitting (LSPIA). LSPIA constructs a series of fitting curves (surfaces) by adjusting the control points iteratively, and the limit curve surface) is the least square fitting result to the given data points. In each iteration, the difference vector for each control point is a weighted sum of some difference vectors between the data points and their corresponding points on the fitting curve (surface). Moreover, we present a simple method to compute the practical weight whose corresponding convergence rate is comparable to that of the theoretical best weight. The advantages of LSPIA are two-fold. First, with LSPIA, a very large data set can be fitted efficiently and robustly. Second, in the incremental data fitting procedure with LSPIA, a new round of iterations can be started from the fitting result of the last round of iterations, thus saving great amount of computation. Lots of empirical examples illustrated in this paper show the efficiency and effectiveness of LSPIA.
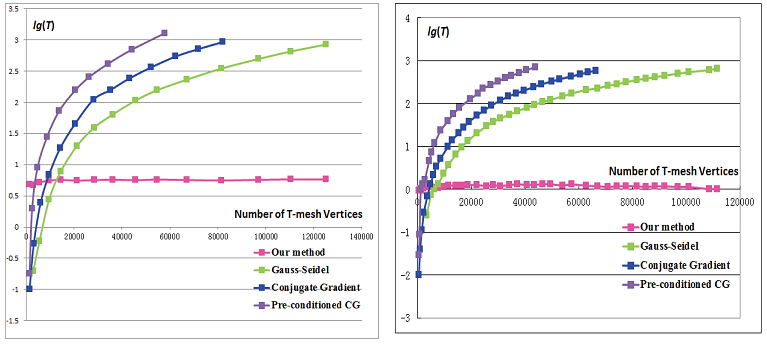
An efficient method for fitting large data sets using T-splines. pdf
SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 35(6), A3052-A3068, 2013.12.
Hongwei Lin, Zhiyu Zhang.
Data fitting is a fundamental tool in scientific research and engineering applications. Generally, there are two ingredients in solving data fitting problems. One is the fitting representation, and the other is the fitting method. Nowadays, the fitting of larger and larger quantities of data sets requires more compact fitting representation and faster fitting methods. The T-spline is a recently invented spline representation, whose control mesh (T-mesh) allows a row of control points to terminate, thus reducing the number of superfluous control points in the B-spline representation significantly. This property makes T-splines more compact than B-splines in fitting large data sets. However, the adaptivity of the T-spline causes the coefficient matrix of a least-squares fitting linear system to lose its block structure. Thus, when fitting large data sets with T-splines by iterative methods, only point iterative methods can be used, and the iteration speeds of typically employed point iterative methods are rapidly slowed with the increasing number of unknowns. In this paper, we present aprogressive T-spline data fittingalgorithm for fitting large data sets with a T-spline representation. As an iterative method, the iteration speed of our method is steady and insensitive to the growing number of unknown T-mesh vertices; thus, it is able to fit large data sets efficiently. Additionally, our method can handle data sets with or without holes in a unified framework, without any special processing. Finally, we apply the progressive T-spline data fitting algorithm in largeimage fitting to validate its efficiency and effectiveness.
Consistency and convergence properties of the isogeometric collocation method. pdf
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 267, 471–486, 2013. 12.
Hongwei Lin, Qianqian Hu, Yunyang Xiong.
Isogeometric collocation (IGA-C) method has shown its superior behavior over Galerkin method in terms of accuracy-to-computational-time ratio and other aspects. However, relatively little has been published about numerical analysis of the IGA-C method. This paper develops theoretical results on consistency and convergence of the IGA-C method to a generic boundary (initial) problem. It shows that the IGA-C method is convergent when differential operator of the boundary (initial) problem is stable or strongly monotone. Finally, we show some concrete examples whose differential operators are strongly monotone, and the IGA-C method is convergent. Moreover, 2D and 3D numerical examples are presented.
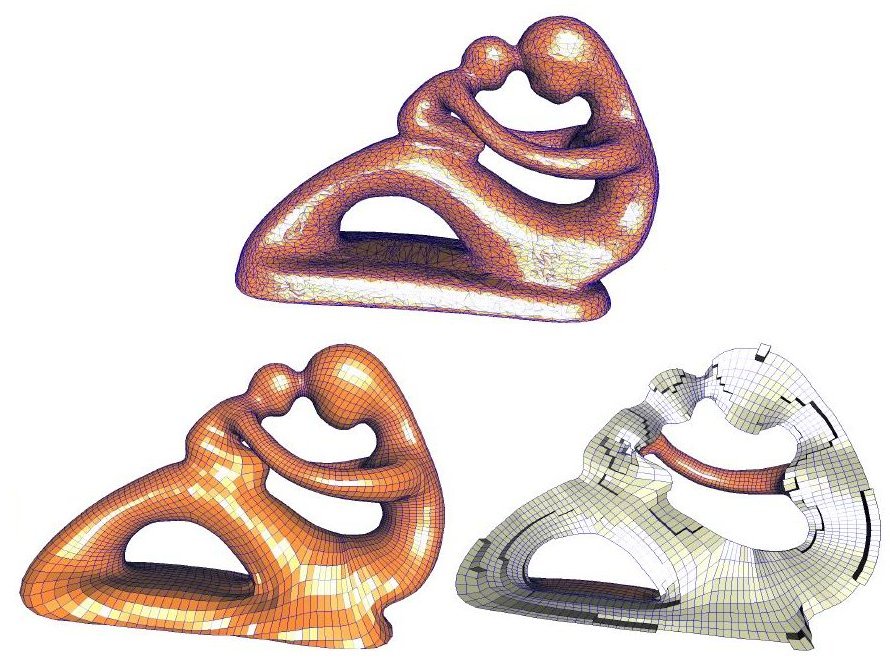

Filling Triangular Mesh Model with All-Hex Mesh by Volume Subdivision Fitting.pdf
Technical Report, TR-ZJUCAD-2012-002, Zhejiang University
Hongwei Lin, Hongwei Liao, Chongyang Deng
The hexahedral mesh (hex mesh) is preferred to the tetrahedral mesh (tet mesh) in finite element methods for numerical simula- tion. However, generating a hex mesh with desirable qualities of- ten requires significant geometric decomposition and considerable user interactions. Therefore, this process may require days or even weeks in the case of complex shapes. In this paper, we develop a method based on subdivision fitting to fill a given triangular mesh model with an all-hex volume mesh. Our method first constructs an initial control solid, which consists of a face-to-face combination of several cubes, based on the skeleton of the given model. The orientation of each cube is determined by the local orientation of the skeleton and the local shape of the given model. Therefore, the shape of the control solid is close to that of the given model. Next, the surface mesh of the initial control solid is extracted and fitted to the given mesh model by an iterative subdivision fitting method. In each iteration, the movement of the surface mesh is diffused to the inner vertices by an optimization technique. After the iteration stops, an all-hex volume mesh that fills the given triangular mesh model can be generated by subdividing the control solid with the multi-linear cell-averaging (MLCA) volume subdivision rule. The smoothness of the MLCA subdivision rule guarantees that the qual- ity of the generated all-hex volume mesh is good. Empirical data show that our algorithm is effective and efficient.
Uniform B-spline Curve Interpolation with Prescribed Tangent and Curvature Vectors.pdf
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 18(9), 1474-1487, 2012.. (SCI/EI)
S. Okaniwa, A. Nasri, Hongwei Lin, A. Abbas, Y. Kineri, T. Maekawa
This paper presents a geometric algorithm for the generation of uniform cubic B-spline curves interpolating a sequence of data points under tangent and curvature vectors constraints. To satisfy these constraints, knot insertion is used to generate additional control points which are progressively repositioned using corresponding geometric rules. Compared to existing schemes, our approach is capable of handling plane as well as space curves, has local control, and avoids the solution of the typical linear system. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is illustrated through several comparative examples. Applications of the method in NC machining and shape design are also outlined.
Extended T-mesh and Data Structure for the Easy Computation of T-spline.pdf
Journal of Information and Computational Science, 9(3), 583-593, 2012. (EI)
Hongwei Lin, Ye Cai, Shuming Gao
T-spline overcomes the topological constraints of the control net of NURBS model successfully. However, the introduction of T-junctions, L-junctions and the isolated vertices in the T-mesh makes its topological structure very flexible. As a result, not only the T-mesh is hard to be represented, but the computation and local refinement of T-spline are difficult to be implemented as well. This hinders the studies and applications of T-splines in practice. In this paper, we develop the extended T-mesh, which can be represented in an obj -like format file, and converted into the face-edge-vertex data structure conveniently. With such data structure, the computation of T-splines can be made much easier. Furthermore, we develop a new local refinement algorithm, by virtue of the extended T-mesh. The new algorithm is easy to be implemented, by separating the local refinement into two procedures, the mesh refinement, and blending function refinement.
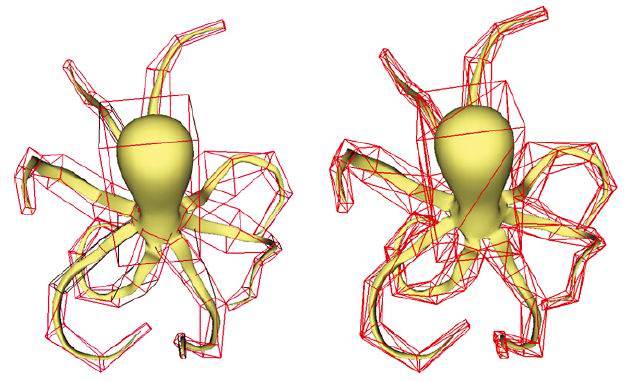
Automatic cage generation by improved OBBs for mesh deformation.pdf
The Visual Computer, Volume 28, Number 1, 21-33, 2012. (SCI/EI)
Chuhua Xian, Hongwei Lin, Shuming Gao
In cage-based deformation, the most tedious task is to construct the coarse cage bounding a model. Currently, the coarse cage is constructed mainly by hand, and the construction usually takes several hours, even longer. Therefore, it is important to develop a convenient method to generate the coarse cage bounding a model. In this paper, we devise a method to construct the coarse cage automatically using the improved OBB tree, while allowing the users to modify the cage easily. Firstly, the OBB tree bounding the model is generated, where we propose an improved OBB slicing rule to make the generated OBBs close to the model it contains. Secondly, the OBBs are adjusted and merged into a whole entity by the boolean union operation. Finally, the outer surface of the entity is extracted as the coarse cage. Empirical results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the automatic coarse cage-generation method.
Variational progressive-iterative approximation for fairing curve and surface generation.pdf
In Proceedings of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics’2011, 258-261, Jinan, China, 2011. (EI)
Hongwei Lin, Yu Zhao
Fairing curve and surface generation is an important topic in geometric design. However, the conventional method for generating the fairing curve and surface, which fit the giving data points, is hard to control the fitting precision, because it is a minimization problem where the objective function is the weighted sum of a fitting term and a fairness term. In this paper, we develop the variational progressive-iterative approximation (abbr. variational PIA) method for fitting a data point sequence. While the variational PIA is easy to control the fitting precision, the generated fitting curve or surface is the most fairing one in some scope. Lots of comparisons show that the fairness results of the variational PIA are comparable to that of the conventional method.
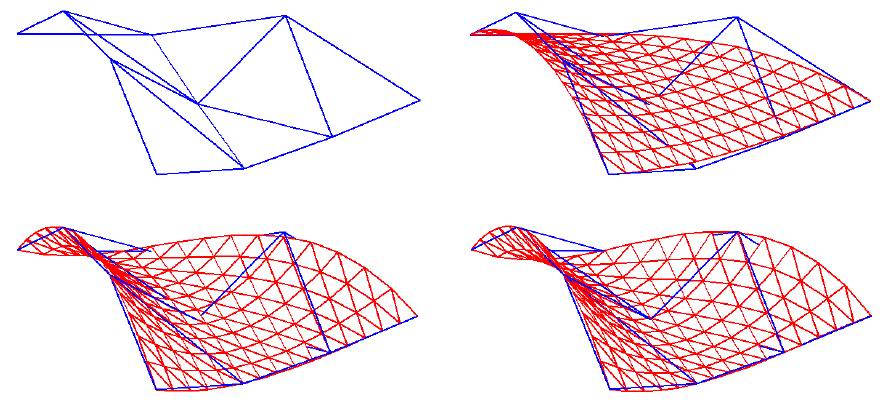
The PIA Property of Low Degree Non-uniform Triangular B-B Patches.pdf
In Proceedings of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics’2011, 239-243, Jinan, China, 2011. (EI)
Hongwei Lin, Yu Zhao
Progressive-iterative approximation presents an intuitive way to generate a sequence of curves or patches, whose limit interpolates the given data points. It has been shown that the blending curves and tensor product blending patches with normalized totally positive basis have the progressiveiterative approximation property. In this paper, we prove that, the quadratic, cubic, and quartic non-uniform triangular Bernstein- B´ezier patches also have the progressive-iterative approximation property. Since the most often empolyed in geometric design are the low degree curves or patches, especially the cubic curves and patches, the result shown in this paper has practical significance for geometric design.
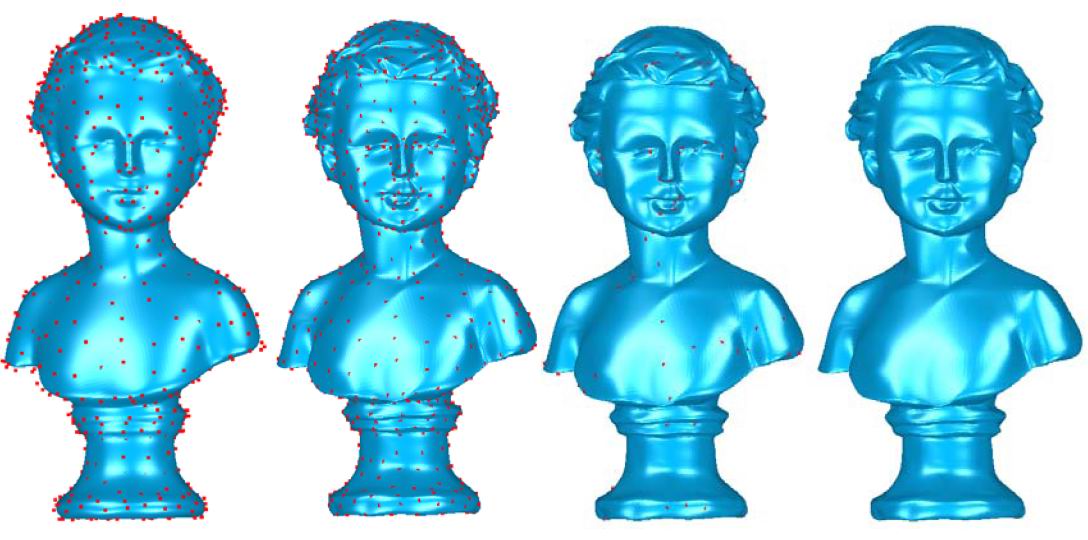

细分曲面拟合的局部渐进插值方法.pdf
计算机研究与发展, 2012第8期. (EI)
赵宇, 蔺宏伟, 鲍虎军
The quality of subdivision surface generated by the approximating scheme is usually better than that by the interpolating scheme, while the approximating subdivision surface is unable to interpolate the vertices of the initial control mesh. Traditional methods that make the approximating subdivision surface interpolate the initial mesh need to solve a global linear system. It is computation intensive, and hard to deal with dense meshes. Without solving a linear system, the progressive interpolation calculates the approximating subdivision surface that interpolates the initial mesh by adjusting the vertices of the control mesh iteratively. It can handle control meshes of any size and any topology while generating smooth subdivision surfaces that faithfully resemble the shape of the initial meshes. In this paper, we show the local property of the progressive interpolation for approximating subdivision schemes. That is, if only a subset of the vertices of the control mesh are adjusted, and others remain unchanged, the limit of the subdivision surface generated in the progressive interpolation procedure still interpolates the corresponding subset of the vertices in the initial mesh. The local property of the progressive interpolation brings more flexibility for shape controlling, and makes the adaptive fitting possible. Lots of experimental examples presented in this paper illustrate the shape controlling and adaptive fitting capabilities of the local progressive interpolation.
基于GPU和区间分析的隐式曲面绘制和网格化.pdf
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 23(5), 763-770, 2011. (EI)
秦阳, 蔺宏伟, 冼楚华, 高曙明
了通过并行化技术提高隐式曲面绘制和网格化的速度,提出一种基于GPU并行计算架构的区间分析方法来网格化和绘制隐式曲面.首先按照给定的绘制分辨率将绘制空间离散成体素表示,充分利用GPU的并行计算能力,采取Ⅸ间分析方法并行计算隐函数在所有体素上的取值区间,从而确定出包含隐函数零等值面的特征体索;进一步,抽取特征体素的外表面对其进行拓扑校正,确保得到的网格是二维流形f然后使用Laplace操作对这个网格进行光滑处理,得到隐式曲面的网格表示.大量实验结果表明,隐式曲面的网格化和绘制时间一般小于0.1s,达到了实时化的水平.
An extended iterative format for the progressive-iteration approximation.pdf
Computers & Graphics, 35(5), 967-975, 2011. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin, Zhiyu Zhang
Progressive-iteration approximation (PIA) is a new data fitting technique developed recently for blending curves and surfaces. Taking the given data points as the initial control points, PIA constructs a series of fitting curves (surfaces) by adjusting the control points iteratively, while the limit curve (surface) interpolates the data points. More importantly, progressive-iteration approximation has the local property, that is, the limit curve (surface) can interpolate a subset of data points by just adjusting a part of corresponding control points, and remaining others unchanged. However, the current PIA format requires that the number of the control points equals that of the data points, thus making the PIA technique inappropriate to fitting large scale data points. To overcome this drawback, in this paper, we develop an extended PIA (EPIA) format, which allows that the number of the control points is less than that of the given data points. Moreover, since the main computations of EPIA are independent, they can be performed in parallel efficiently, with storage requirement O(n), where n is the number of the control points. Therefore, due to its local property and parallel computing capability, the EPIA technique has great potential in large scale data fitting. Specifically, by the EPIA format, we develop an incremental data fitting algorithm in this paper. In addition, some examples are demonstrated in this paper, all implemented by the parallel computing toolbox of Matlab, and run on a PC with a four-core CPU.
CAD mesh model segmentation by clustering.pdf
Computers & Graphics, 35(3), 685-691, 2011 (SCI/EI)
Dong Xiao, Hongwei Lin, Chuhua Xian, Shuming Gao
CAD mesh models have been widely employed in current CAD/CAM systems, where it is quite useful to recognize the features of the CAD mesh models. The first step of feature recognition is to segment the CAD mesh model into meaningful parts. Although there are lots of mesh segmentation methods in literature, the majority of them are not suitable to CAD mesh models. In this paper, we design a mesh segmentation method based on clustering, dedicated to the CAD mesh model. Specifically, by the agglomerative clustering method, the given CAD mesh model is first clustered into the sparse and dense triangle regions. Furthermore, the sparse triangle region is separated into planar regions, cylindrical regions, and conical regions by the Gauss map of the triangular faces and Hough transformation; the dense triangle region is also segmented by the mean shift operation performed on the mean curvature field defined on the mesh faces. Lots of empirical results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the CAD mesh segmentation method in this paper.
Curvature of singular Bézier curves and surfaces.pdf
Computer Aided Geometric Design, 28(4), 233-244, 2011. (SCI/EI)
Sederberg T. W., Hongwei Lin, Xin Li
This paper presents a general approach for finding the limit curvature at a singular endpoint of a rational Bézier curve and the singular corner of a rational Bézier surface patch. Conditions for finite Gaussian and mean limit curvatures are expressed in terms of the rank of a matrix.
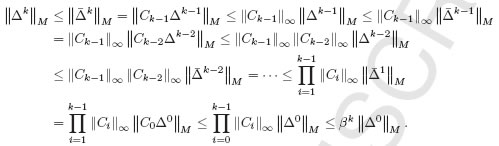
The convergence of the geometric interpolation algorithm. pdf
Computer-Aided Design (2010), doi:10.1016/j.cad.2010.01.006 (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin
the geometric interpolation algorithm is proposed by Maekawa et. al. in Interpolation by geometric algorithm, Computer-Aided Design, 39, 313-323, 2007. Without solving a system of equations, the algorithm generates a curve(surface) sequence, of which the limit curve(surface) interpolates the given data points. However, the convergence of the algorithm is a conjecture in the reference above, and demonstrated by lots of empirical examples. In this paper, we prove the conjecture given in the reference in theory, that is, the geometric interpolation algorithm is convergent for a blending curve(surface) with normalized totally positive basis, under the condition that the minimal eigenvalue λmin(Dk) of the collocation matrix Dk of the totally positive basis in each iteration satisfies λmin(Dk) >α> 0. As a consequence, the geometric interpolation algorithm is convergent for Bezier, B-spline, rational Bezier, and NURBS curve(surface) if they satisfy the condition aforementioned, since Bernstein basis and B-spline
basis are both normalized totally positive.
Local progressive-iterative approximation format for blending curves and patches. pdf
Computer Aided Geometric Design (2010), doi:10.1016/j.cagd.2010.01.003 (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin
Just by adjusting the control points iteratively, progressive-iterative approximation presents an intuitive and straightforward way to fit data points. It generates a curve or patch sequence with finer and finer precision, and the limit of the sequence interpolates the data points. The progressive-iterative approximation brings more flexibility for shape controlling in data fitting. In this paper, we design a local progressive-iterative approximation format, and show that the local format is convergent for the blending curve with normalized totally positive basis, and the bi-cubic B-spline patch, which is the most commonly used patch in geometric design. Moreover, a special adjustment manner is designed to make the local progressive-iterative approximation format is convergent for a generic blending patch with normalized totally positive basis. The local progressive-iterative approximation format adjusts only a part of the control points of a blending curve or patch, and the limit curve or patch interpolates the corresponding data points. Based on the local format, data points can be fit adaptively.
Bisection approach for pixel labelling problem. pdf
Pattern Recognition 43, 1826–1834, 2010. (SCI/EI)
Dengfeng Chai, Hongwei lin , Qunsheng Peng
this paper formulates pixel labelling as a series of two-category classification. Unlike existing techniques, which assign a determinate label to each pixel, we assign a label set to each pixel and shrink the label set step by step. Determinate labelling is achieved within log2n (n is size of label set) steps. In each step, we bisect the label set into two subsets and discard the one with higher cost of assigning it to the pixel. Simultaneous labelling of an image is carried out by minimizing an energy function that can be minimized via graph cut algorithm. Based on the bisection approach, wep ropose a bitwise algorithm for pixel labelling, which set one bit of each pixel’s label in each step. We apply the proposed algorithm to stereo matching and image restoration. Experimental results demonstrate that both good performance and high efficiency are achieved.
FEA-mesh editing with feature constrained. pdf
Proceedings of CAD/CG’09.
Chuhua Xian, Shuming Gao, Hongwei Lin, and Dong Xiao.
this paper proposes a framework for FEA-mesh editing with feature constrained. In the framework, cage-based technique is first used to edit the base-decomposition model. Vertices of the constrained featureare transformed into a local form, and then reconstructed after determining the common boundary. Feature rotation constraint derives from the normal change of the boundary plane. Parameters are analyzed before editing operation, and our method permits the user to add constraints on the parameters of the feature. This framework can also keep consistence for the disconnected assembly mesh model. Experimental results show that constrained features hold precisely after mesh editing. Additionally, experimental datav alidate the efficiency of our method, achieving real-time response.
Automatic generation of coarse bounding cages from dense meshes. pdf
IEEE International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications 2009, 21-27.
Chuhua Xian, Hongwei Lin, Shuming Gao.
the coarse bounding cage of a dense mesh plays important roles in computer graphics, computer vision, and geometric design. Specifically, in volume-based deformation, a coarse bounding cage is required to manipulate the dense mesh model it enclosed; in subdivision surface fitting, the fitting starts from a coarse cage bounding the fitted dense mesh or point set; and so on. However, the generation of a coarse bounding cage is mainly by interactive ways, which are very tedious and time-consuming. In this paper, we develop a fully automatic method to generate a coarse cage bounding a dense mesh model. the automatically generated coarse bounding cage can keep the topological structure and major geometric features of the original mesh model, which is validated by theoretical analysis and experimental data presented in this paper. Further more, we employ the automatically generated coarse bounding cage in some applications, such as deformation, and subdivision fitting, producing good results.
On the derivative formula of a rational Bezier curve at a corner. pdf
Applied Mathematics and Computation, 210(1), 197-201, 2009.(SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin
In this paper, we develop the exact arbitrary order derivative formula of a rational Bezier curve at its corner. Some examples are presented to demonstrate the computation of the exact derivatives.
Poisson based reuse of freeform features with NURBS representation. pdf
Computers in Industry, 60(1), 64-74, 2009. (SCI/EI)
Wei Zhao, Shuming Gao, Yusheng Liu, Hongwei Lin.
the effective reuse of freeform features represented by NURBS is still an open issue. In this paper, a novel approach to the reuse of freeform features with NURBS representation is proposed. Firstly, the conditions for preserving differential properties of reused freeform features are derived, and a reuse-oriented representation of freeform features is put forward. Based on them, a reuse algorithm of freeform features is developed, which adopts Poisson equation, knots insertion and degree elevation to achieve the preservation of the differential geometry properties and the adaptability. The approach is implemented and some examples are given.
A Simple Method for Approximating Rational Bezier Curve Using Bezier Curves. pdf
Computer Aided Geometric Design, 25(8), 697-699 , 2008. (SCI/EI)
Youdu Huang, Huaming Su, Hongwei Lin.
this paper presents a simple method for approximating a rational Bézier curve with Bézier curve sequence, whose control points are those of degree-elevated rational Bézier curves. It is proved that the derivatives with any given degree of the Bézier curve sequence constructed this way would niformly converge to the corresponding derivatives of the original rational Bézier curve.
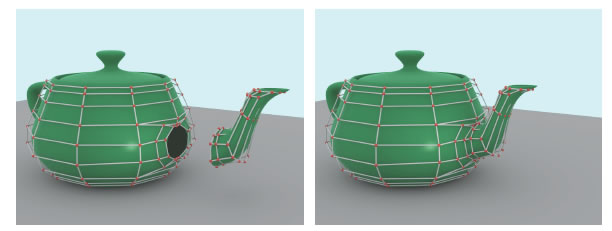
Watertight trimmed NURBS. pdf
ACM transactions on Graphics, 27(3), 2008. (SCI/EI)
thomas W. Sederberg, G. Thomas Finnigan, Xin Li, Hongwei Lin, Heather Ipson.
this paper addresses the long-standing problem of the unavoidable gaps that arise when expressing the intersection of two NURBS surfaces using conventional trimmed-NURBS representation. the solution converts each trimmed NURBS into an untrimmed T-Spline, and then merges the untrimmed T-Splines into a single, watertight model. the solution enables watertight fillets of NURBS models, as well as arbitrary feature curves that do not have to follow isoparameter curves. the resulting T-Spline representation can be exported without error as a collection of NURBS surfaces.
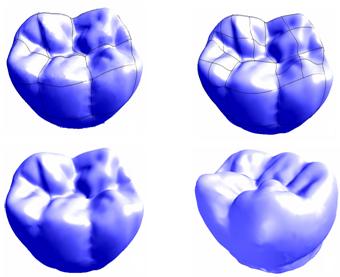
Adaptive Patch-based Mesh Fitting in Reverse Engineering. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 39(12), 1134-1142, 2007.12. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin, Wei Chen, Hujun Bao
In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive mesh fitting algorithm that fits a triangular model with G1 smoothly stitching bi-quintic Bezier patches. Our algorithm first segments the input mesh into a set of quadrilateral patches, whose boundaries form a quadrangle mesh. For each boundary of each quadrilateral patch, we construct a normal curve and a boundary-fitting curve, which fit the normal and position of its boundary vertices respectively. By interpolating the normal and boundary-fitting curves of each quadrilateral patch with a Bezier patch, an initial G1 smoothly stitching Bezier patches is generated. We perform this patch-based fitting scheme in an adaptive fashion by recursively subdividing the underlying quadrilateral into four sub-patches. The experimental results show that our algorithm achieves precision-ensured Bezier patches with G1 continuity and meets the requirements of reverse engineering.
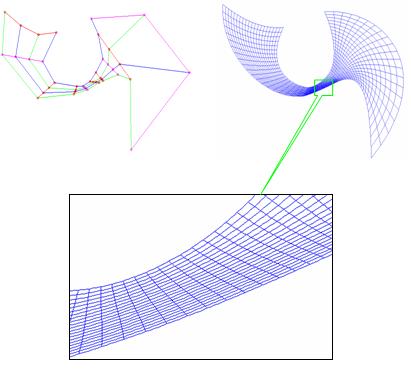
Generating strictly non-self-overlapping structured quadrilateral grids. pdf
Computer-Aided Design. 39(9), 709-718, 2007.9. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin, Kai Tang, Ajay Joneja, Hujun Bao.
In this paper, we present a BPM (Bezier patch mapping) algorithm which generates a strictly non-self-overlapping structured quadrilateral grid in a given four-sided planar region. Given four pieces of polynomial curves which enclose a simple region in the plane, the algorithm first constructs a Bezier patch which interpolates the four curves (as its four boundary curves), while the inner control points of its control grid remain unknown. In this paper, we show that, for the bijective condition to be satisfied, it is sufficient that the interior points satisfy a set of quadratic inequality equations. Exploiting this key result, we formulate the mapping algorithm as an optimization problem where the constraints are the bijective condition of the Bezier patch mapping (BPM), and the objective is to find out the best from all of the non-self-overlapping grids. thus, commercial optimization solvers can be used to find the bijective mapping. If a solution to the optimization problems exists, then so does a solution to the mapping problem, and vice-versa. the BPM method is simple and intuitive, and some examples presented in this paper demonstrate its effectiveness.
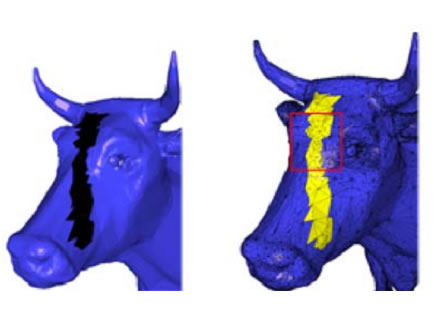
A Robust Hole-Filling Algorithm for Triangular Mesh. pdf
the Visual Computer, 23(12), 987-997, 2007.12. (SCI/EI)
Wei Zhao, Shuming Gao, Hongwei Lin.
this paper presents a novel hole-filling algorithm that can fill arbitrary holes in triangular mesh models. First, the advancing front mesh technique is used to cover the hole with newly created triangles. Next, the desirable normals of the new triangles are approximated using our desirable normal computing schemes. Finally, the three coordinates of every new vertex are re-positioned by solving the Poisson equation based on the desirable normals and the boundary vertices of the hole. Many experimental results and error evaluations are given to show the robustness and efficiency of the algorithm.
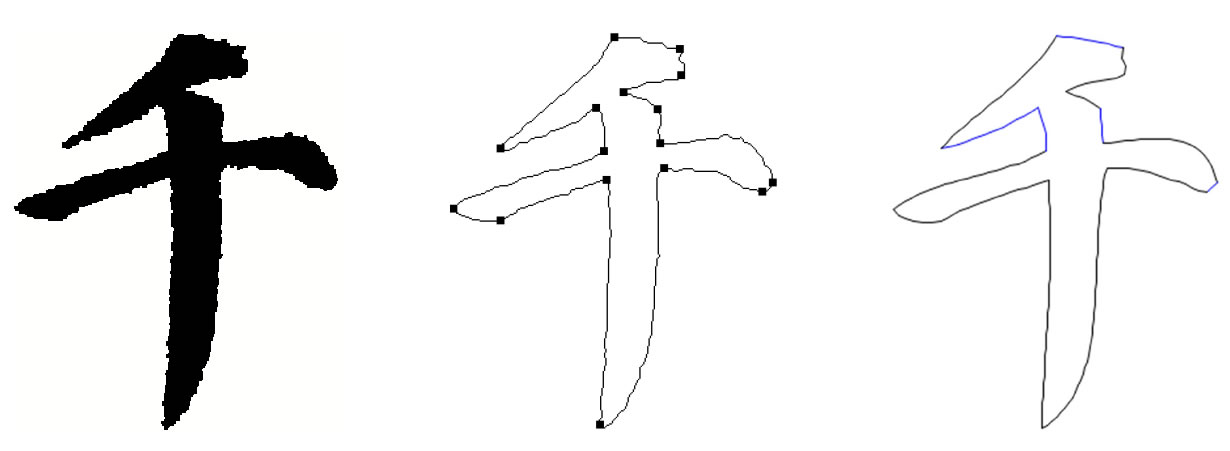
A novel method for vectorizing historical documents of Chinese calligraphy. pdf
In Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, Beijing, China, 219-224, 2007.10. (EI/ISTP)
Junsong Zhang, Hongwei Lin, Jinhui Yu.
We develop a novel method for feature point detection and employ it to generate outline font from historical document of Chinese calligraphy. the feature points at a character contour subdivide the contour into segments. Each segment can be then fitted by a parametric curve to obtain the outline font. Some experimental results are also presented in the paper.
Parameterization for Fitting Triangular Mesh. pdf
Progress in Natural Science, 16 (11), 1214-1221, 2006.11. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei lin, Guojin Wang, Ligang Liu, Hujun Bao.
In reverse engineering, in order to fit a piece of NURBS surface to a triangular mesh surface with four boundaries, the triangular mesh surface needs to be parameterized into a unit square parameter field firstly. Obviously, more uniform distribution of the obtained regular parametric curve grid leads to better fitting surface to the triangular mesh. Due to the uniform distribution of the smooth isotherms in the steady temperature field defined on the triangular mesh surface, the isotherms can act as the iso-parametric curves quite well. However, it is hard to directly solve the 2-dimensional quasi-harmonic equation defined on a triangular mesh surface for getting the steady temperature field on the mesh surface. In this paper, we present a novel method to parameterize an arbitrary triangular mesh surface using the steady temperature field. that is, we construct a lamina with the triangular mesh surface as its border surface firstly; and then calculate the 3-dimensional harmonic equation on the lamina; finally, we can get the steady temperature field defined on the triangular mesh surface. Based on the temperature field, the triangular mesh surface can be parameterized into the unit square parameter field.
Modified Affine Arithmetic in Tensor Form for trivariate Polynomial Evaluation and Algebraic Surface Plotting. pdf
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 195(1-2), 155-171, 2006.9. (SCI/EI)
Huahao Shou, Hongwei lin, Ralph Martin, Guojin Wang.
this paper extends the modified affine arithmetic in matrix form method for bivariate polynomial evaluation and algebraic curve plotting in 2D to modified affine arithmetic in tensor form for trivariate polynomial evaluation and algebraic surface plotting in 3D. Experimental comparison shows that modified affine arithmetic in tensor form is not only more accurate but also much faster than standard affine arithmetic when evaluating trivariate polynomials.
Conditions for Determining the Regularity of Bézier Curve and Surface. pdf
Journal of Software, 17(3), 516-524, 2006.3. (EI)
Hongwei Lin, Qing Wang, Hujun Bao.
Regularity is an important algebraic property of parametric curve and surface, which depends on the parameterization of parametric curve and surface. In computer-aided manufacturing, the processed parametric curve and surface should be regular, so the parametric curve and surface generated by computer-aided design should be regular first. However, the computation of determining the regularity of parametric curve and surface by solving equation or system of equations induced by the definition of regularity is considerably complex, and is actually infeasible. In this paper, by transforming the parametric representations of derivative vector curve (of Bézier curve) and normal vector surface (of Bézier surface) to their implicit representations, a simple and practical sufficient condition for determining the regularity of Bézier curve and surface is presented.
Totally Positive Bases and Progressive Iteration Approximation. pdf
Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 50(3-4), 575-586, 2005.4. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei lin, Hujun Bao, Guojin Wang.
In this paper, we study the progressive iteration approximation property of a curve (tensor product surface) generated by blending a given data point set and a set of basis functions. the curve (tensor product surface) has the progressive iteration approximation property as long as the basis is totally positive and the corresponding collocation matrix is non-singular. Thus, the B-spline and NURBS curve (surface) have the progressive iteration approximation property, and Bézier curve (surface) also has the property if the corresponding collocation matrix is non-singular.
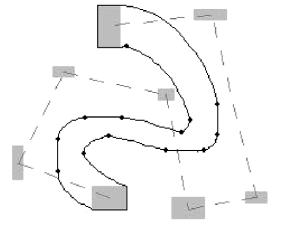
Curve Reconstruction Based on an Interval B-spline Curve. pdf
the Visual Computer, 21(6), 418-427, 2005.6. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei lin, Wei Chen, Guojin Wang.
Curve reconstruction that generates a piece of centric curve from a piece of planar strip-shaped point cloud, is a fundamental problem in reverse engineering. In this paper, we present a new curve reconstruction algorithm based on interval B-spline curve. The algorithm constructs a rectangle sequence approximating the point cloud using a new data clustering technique, which facilitates the determination of curve order implied in the shape of the point cloud. A quasi-centric point sequence and two pieces of boundary point sequences are then computed, based on which a piece of interval B-spline curve that represents the geometric shape of the point cloud is constructed. Its centric curve is the final reconstructed curve. The whole algorithm is intuitive, simple and efficient as demonstrated by experimental results.
Constructing Iterative Non-Uniform B-spline Curve and Surface to Fit Data Points. pdf
SCIENCE IN CHINA, Series F, 47(3), 315-331, 2004.3. (SCI)
Hongwei lin, Guojin Wang, Chenshi Dong.
In this paper, based on the idea of profit and loss modification, we present the iterative non-uniform B-spline curve and surface to settle a key problem in computer aided geometric design and reverse engineering, that is, constructing the curve (surface) fitting (interpolating) a given ordered point set without solving a linear system. We start with a piece of initial non-uniform B-spline curve(surface) which takes the given point set as its control point set. Then by adjusting its control points gradually with iterative formula, we can get a group of non-uniform B-spline curves (surfaces) with gradually higher precision. In this paper, using modern matrix theory, we strictly prove that the limit curve (surface) of the iteration interpolates the given point set. The non-uniform B-spline curves (surfaces) generated with the iteration have many advantages, such as satisfying the NURBS standard, having explicit expression, gaining locality, and convexity preserving, etc.

A Mesh Reconstruction Algorithm Driven by Intrinsic Property of Point Cloud. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 36(1), 1-9, 2004.1. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei lin, C. L. Tai, Guojin Wang.
this paper presents an algorithm for reconstructing a triangle mesh surface from a given point cloud. Starting with a seed triangle, the algorithm grows a partially reconstructed triangle mesh by selecting a new point based on an intrinsic property of the point cloud, namely, the sampling uniformity degree. The reconstructed mesh is essentially an approximate minimum-weight triangulation to the point cloud constrained to be on a two-dimensional manifold. thus, the reconstructed surface has only small topological difference from the surface of the sampled object. Topological correct reconstruction can be guaranteed by adding a post-processing step.
G1 Continuous Interpolation Curve on Smooth Surface. pdf
Journal of Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, 15(5), 541-546, 2003.5. (EI)
Hongwei lin, Guojin Wang.
In computer graphics and computer aided geometric design, the techniques of generating an interpolation curve that is restricted on a given smooth surface and holds geometric continuity have shown more and more wide applications. We propose an approach of constructing Bézier spline curve of degree 3 to interpolate the given points on the smooth surface and then project the curve onto this surface with ruled surface. the projected curve keeps G1 continuity. Theoretical deduction and experimentation show that such an approach is effective and produces good results.
Three Dimensional Signed Euclidean Distance Transform and Its Applications. pdf
Chinese Journal of Computers, 26(12), 1645-1651, 2003.12.
Hongwei Lin, Guojin Wang.
the researches for distance t ransform have long history in image processing. In this paper, we extend two dimensional signed distance t ransform to three dimension , optimize it and analyze its computational complexity. Furthermore , we apply it to computer graphics. Firstly , it can be employed to transform the triangular mesh representation of graphics model into it s distance field representation. By the three dimensional signed distance t ransform on the voxel representation of a graphics model , the global search for the point , which is closest to a given space point and on the graphical model , can be simplified to a local search. It greatly reduces the computational complexity. Secondly, and similarly , it can be employed to calculate the minimum distance between two pieces of surfaces in the space.

Modified affine arithmetic is more accurate than centered interval arithmetic or affine arithmetic. pdf
In Proceedings of 10th IMA Conference on the Mathematics of Surfaces, LECTURE NOTES IN COMPUTER SCIENCE, Leeds, England, 355-365, 2003.9. (SCI)
Huahao Shou, Hongwei Lin, Martin R., Guojin Wang.
In this paper we give mathematical proofs of two new results relevant to evaluating algebraic functions over a box-shaped region: (i) using interval arithmetic in centered form is always more accurate than standard affine arithmetic, and (ii) modified affine arithmetic is always more accurate than interval arithmetic in centered form. Test results show that modified affine arithmetic is not only more accurate but also much faster than standard affine arithmetic. We thus suggest that modified affine arithmetic is the method of choice for evaluating algebraic functions, such as implicit surfaces, over a box.
Boundary Evaluation for Interval Bézier Curve. pdf
Computer-Aided Design, 34(9), 637-646, 2002.9. (SCI/EI)
Hongwei Lin, Ligang Liu, Guojin Wang.
the objective of this paper is to provide an efficient and reliable algorithm for representing and evaluating the boundary of the interval Bezier curve in 2-and 3-D. the boundary of the planar Bezier curve is represented by a sequence of Bezier curve segments with same degree and line segments in the order they are encountered when marching counter-clockwise along its boundary. the boundary can also be represented as a single B-spline curve having the same degree with the interval Bezier curve. the boundary of the 3-D interval Bezier curve is made up of trimmed Bezier surface patches and rectangular patches. Some examples illustrate our algorithms.
Last updated: Nov. 7, 2016.