
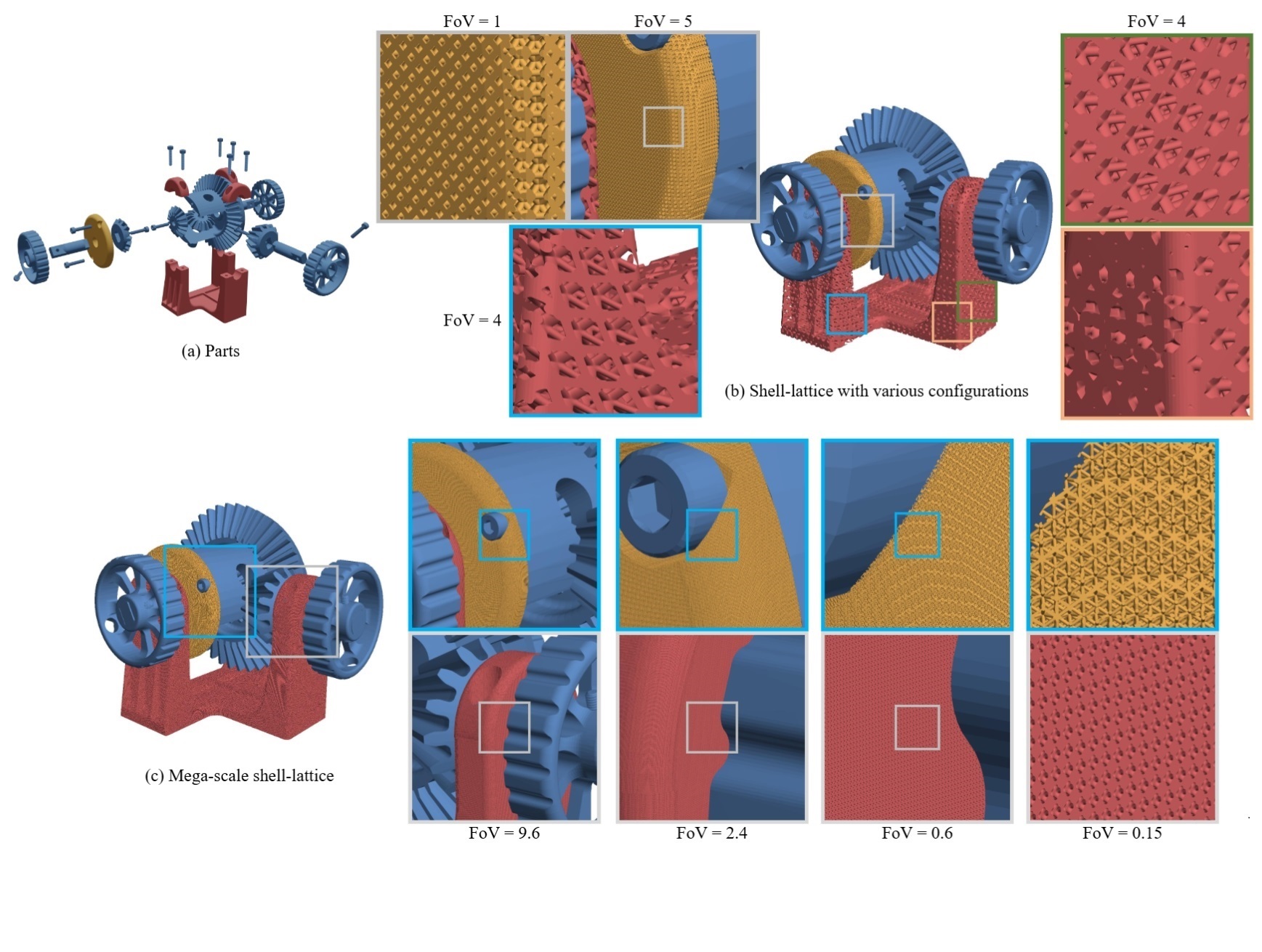
Computer-Aided Design, 2025
We propose an augmented sphere tracing (AST) pipeline that seamlessly integrates editing, rendering, and slicing of mega-scale peri-odic shell-lattice structures. Traditional STL-based pipelines face challenges such as time-consuming format conversions, high storage requirements, and complex blending issues between discrete lattice and shell components, often resulting in a loss of geometric accuracy. AST combines hybrid implicit lattice and mesh shell representations, eliminating the need for explicit 3D model construction and unnecessary geometric format conversions, and supports various types of shell-lattices , including blending, warping, field-directed distributions, region-specific cell types, and produces arbitrary directional slicing for manufacturing. AST archives high efficiency and accuracy in real-time rendering of shell-lattices with billions of beams on an RTX 3090.

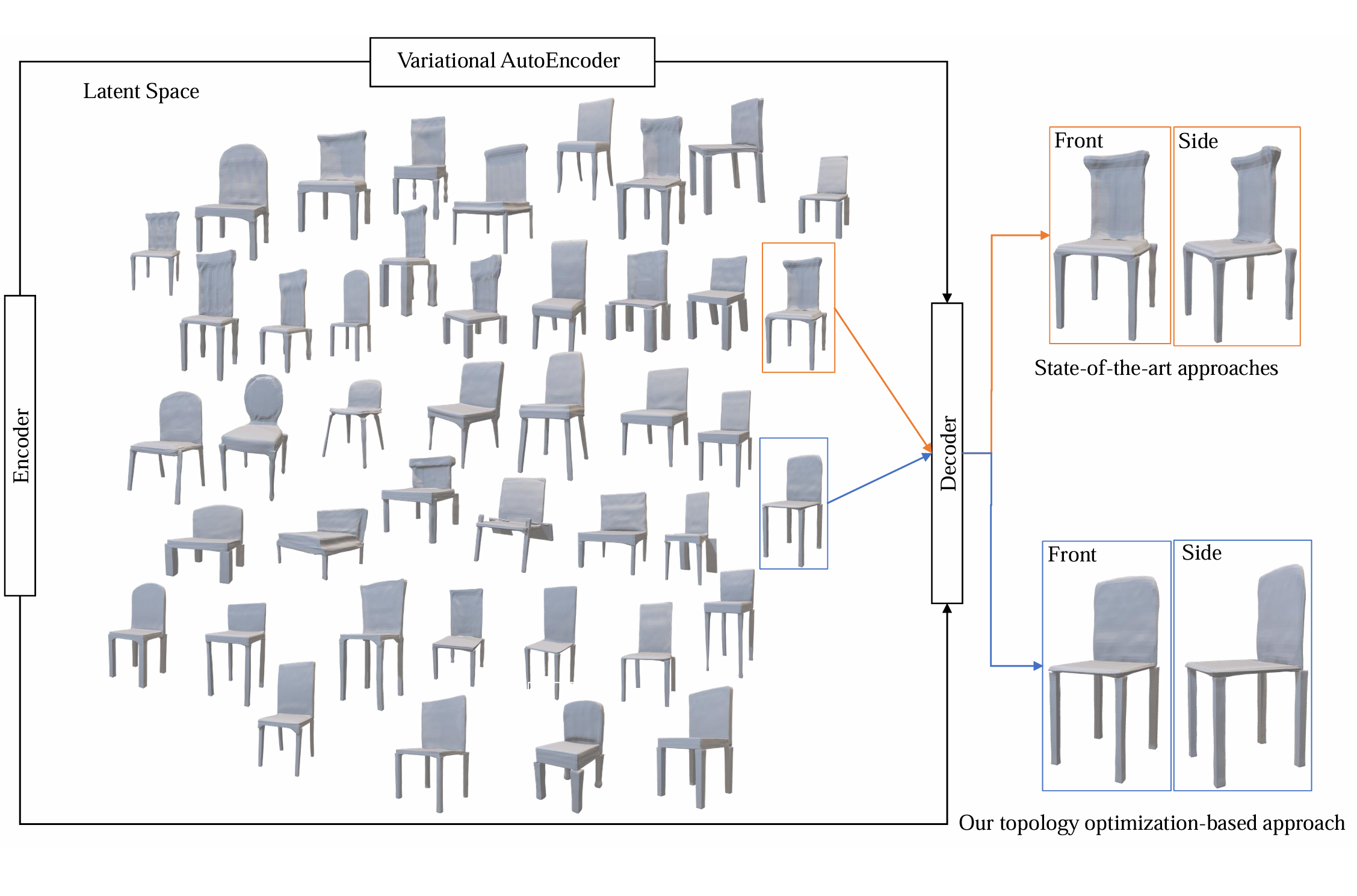
Computer-Aided Design, 2025
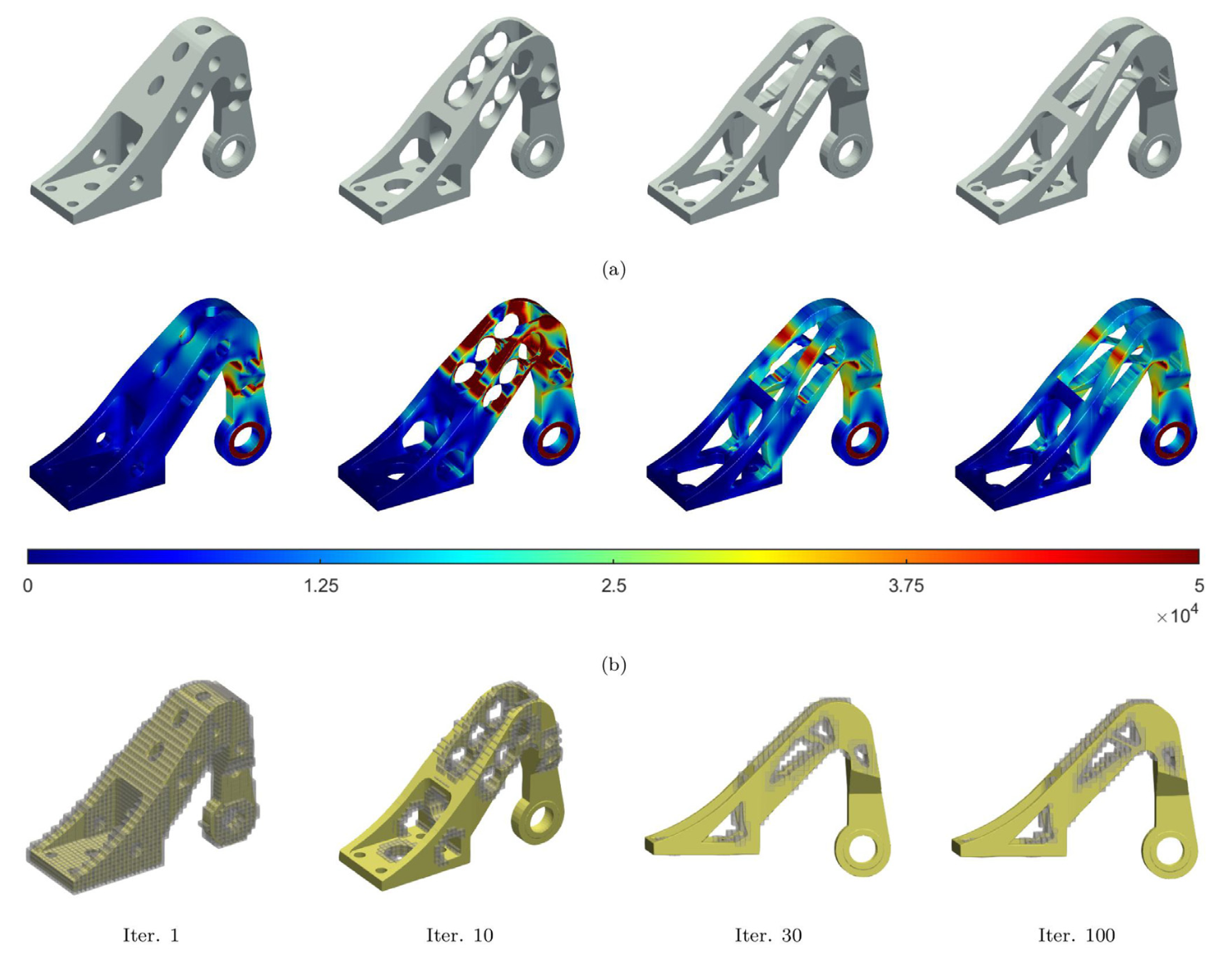
We propose a novel approach to structure-aware topology optimization (SATO) to generate physically plausible multi-component structures with diverse stylistic variations. Our approach leverages variational autoencoders (VAEs) to encode both geometries and corresponding structures into a unified latent space, capturing part arrangement features. The design target is carefully formulated as a topology optimization problem taking the VAE code as design variables under physical constraints, and solved numerically via analyzing the associated sensitivity with respect to the VAE variables. The method enables the generation of diverse and reliable designs, maintaining structural integrity throughout, via a direct smooth interpolation between the optimized designs. ...

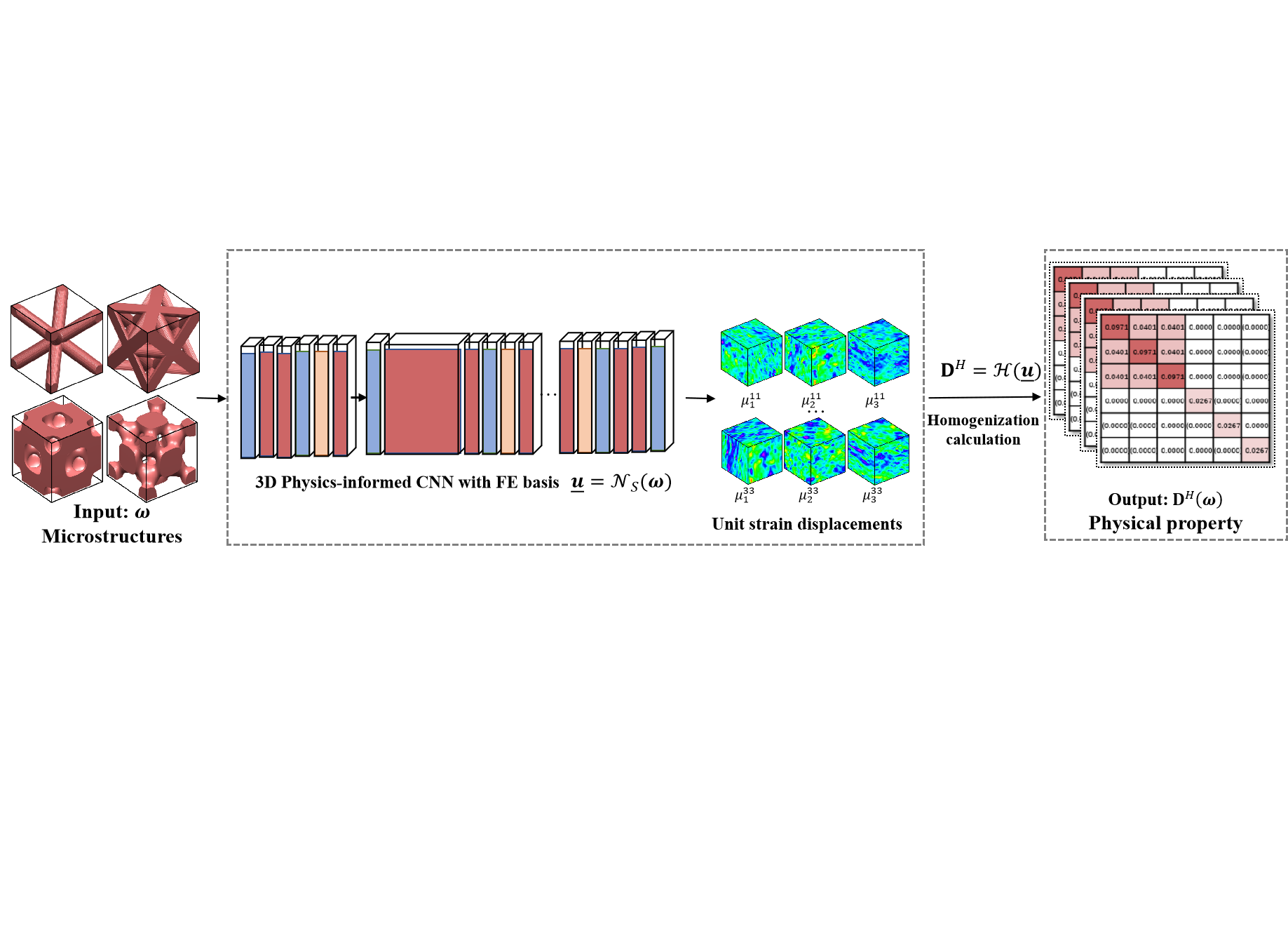
The Visual Computer, 2024
We build a mapping from a 3D microstructure to its effective material property, or called structure-property mapping, using a 3D convolutional neural network(CNN). Unlike the direct approach using labeled simulation data, the mapping is based on the physical knowledge of the structure-property relationship determined by its underlying PDE equations. The knowledge is embedded in the loss function of the CNN framework, which is designed and tested under several different formulations to improve its training convergence. ...


IEEE Trans. Computer Graphics and Visualization, 2024
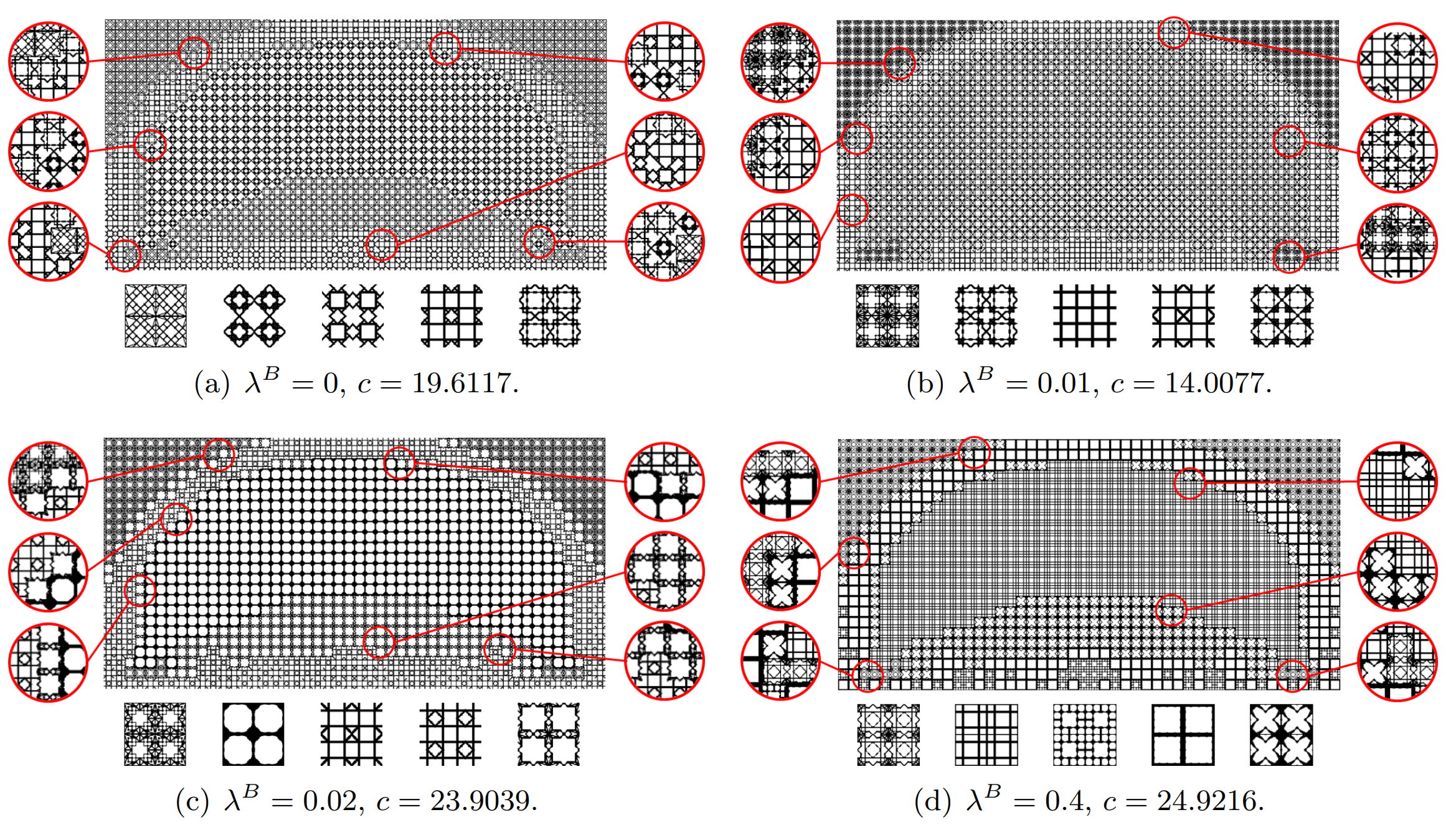
A concept of explicit topology optimization of open-cell Voronoi foams is proposed that can efficiently and reliably guide the foam’s topology and geometry variations under critical physical and geometric requirements. Taking the site (or seed) positions and beam radii as the DOFs, we explore the differentiability of the open-cell Voronoi foams w.r.t. its seed locations, and propose a highly efffcient local ffnite difference method to estimate the derivatives. ... ...

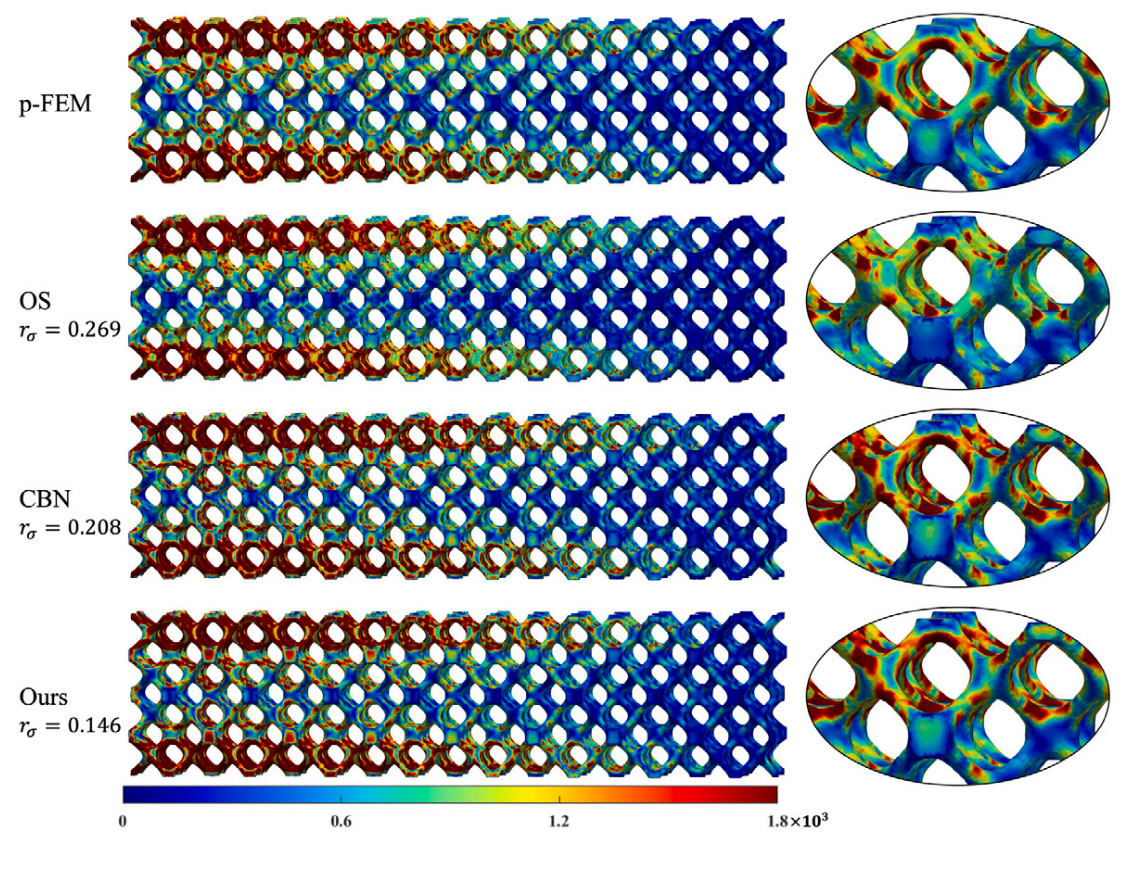
Computers Method in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2024
Numerical coarsening is an approach that constructs coarsened shape (or basis) functions for simulating heterogeneous structures on a coarse mesh, and seeks the fine mesh solution on a finite dimensional space spanned by these shape functions. It avoids the challenging issue of conforming meshing, reduces computational costs while maintaining high simulation accuracy, and has huge potential in the simulation of composites or even complex CAD models in fictitious domain methods ... ...

Computers & Structures, 2023
An optimization method for the design of multi-lattice structures satisfying local buckling constraints is proposed in this study. In order to resolve the highly nonlinear large-scale optimization problem, a consecutive numerical approach is devised: macro-field optimization and microstructure embedding. The macro-field optimization finds an optimal elasticity tensor distribution among all feasible elastic continua based on a concept of free material optimization (FMO), which largely extends the design space compared with density-based topology optimization. During the process, a machine learning approach is also devised to signiffcantly reduce the number of material/lattice types and thus the overall computational costs. Ultimately, a lattice structure under requirements of overall stiffness and local buckling resistance is produced, as demonstrated via numerical examples.

ACM Trans. Graphics (Siggraph) , 2023
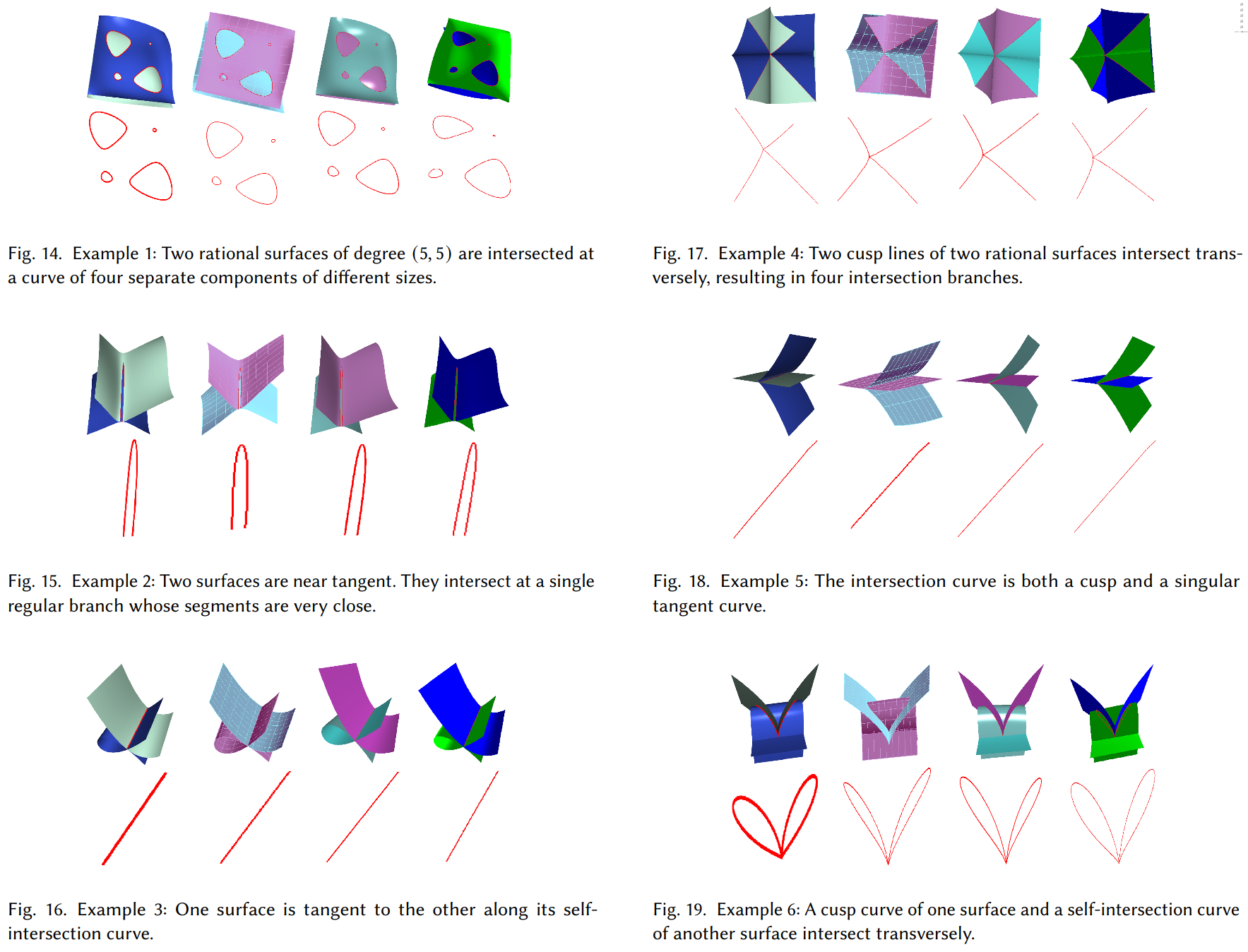
We propose a topology-driven hybrid symbolic-numeric framework to approximate rational parametric surface-surface intersection (SSI) based on a concept of interval algebraic topology analysis (IATA), which conffgures within a 4D interval box the SSI topology. We map the SSI topology to an algebraic system’s solutions within the framework, classify and enumerate all topological cases as a mixture of four fundamental cases (or their speciffc sub-cases). Various complicated topological situations are covered, such as cusp points or curves, tangent points (isolated or not) or curves, tiny loops, self-intersections, or their mixtures. The approach demonstrates improved robustness under benchmark topological cases when compared with available open-source and commercial solutions, including IRIT, SISL, and Parasolid.

Computer Aided Design, 2023
Parametric optimization is an important product design technique, especially in the context of the modern parametric feature-based CAD paradigm. A new method for parametric optimization is introduced, based on a unified model representation scheme called eXtended Voxels (XVoxels). This scheme hybridizes feature models and voxel models into a new concept of semantic voxels, where the voxel part is responsible for FEM solving, and the semantic part responsible for high-level information to capture both design and simulation intents. As such, it can establish a direct mapping between design models and analysis models, which in turn enables automatic updates on simulation results for design modifications, and vice versa—effectively a closed loop between CAD and CAE.


Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2022
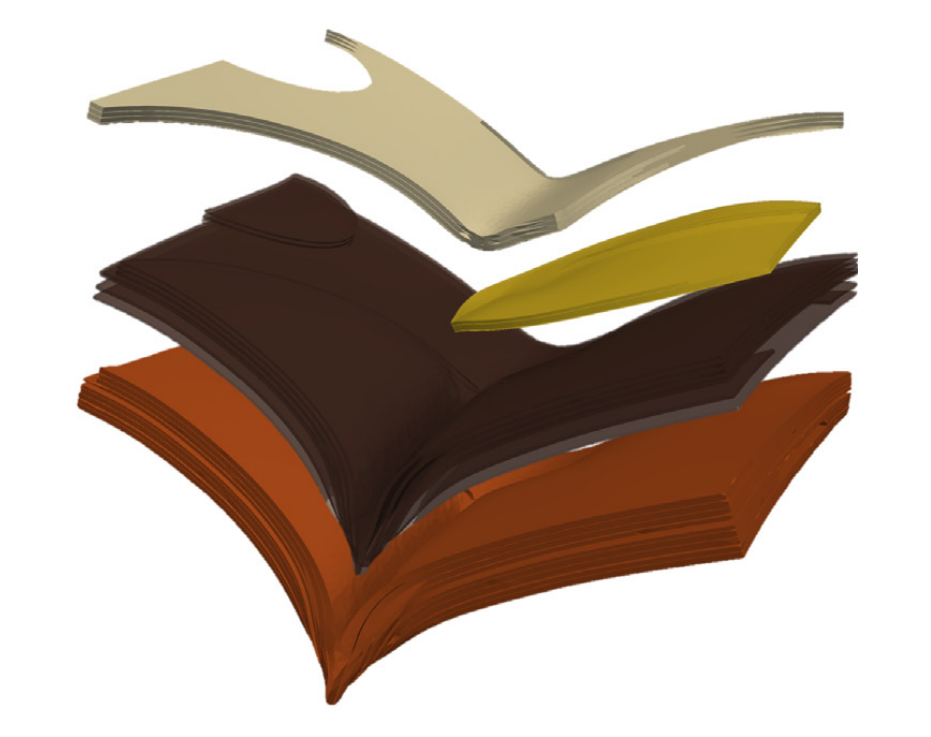
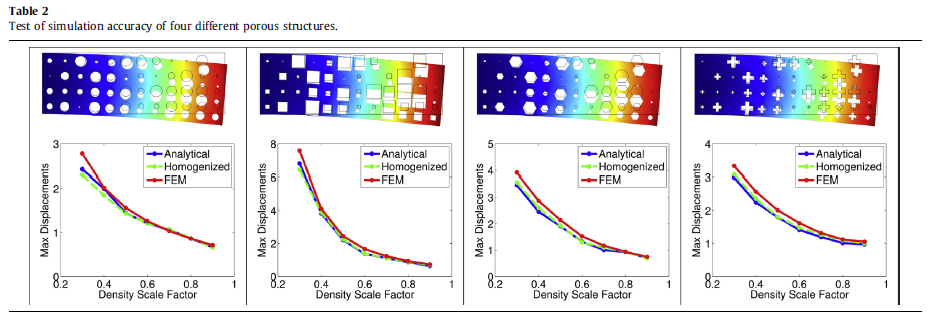
Numerically predicting the performance of heterogeneous structures without scale separation is a challenging task owing to the critical requirements related to computational scalability and efffciency that must be satisffed. This study proposed an approach for constructing new material-aware shape (basis) functions per element for a coarse discretization of the structure considering each curved bridge node (CBN) that is deffned along the boundaries of the elements. The performance was tested and demonstrated through extensive numerical examples, including a 3D industrial example of billions of degrees of freedom, and comparisons with results obtained from classical approaches were made.

Journal of Computational Physics, 2021
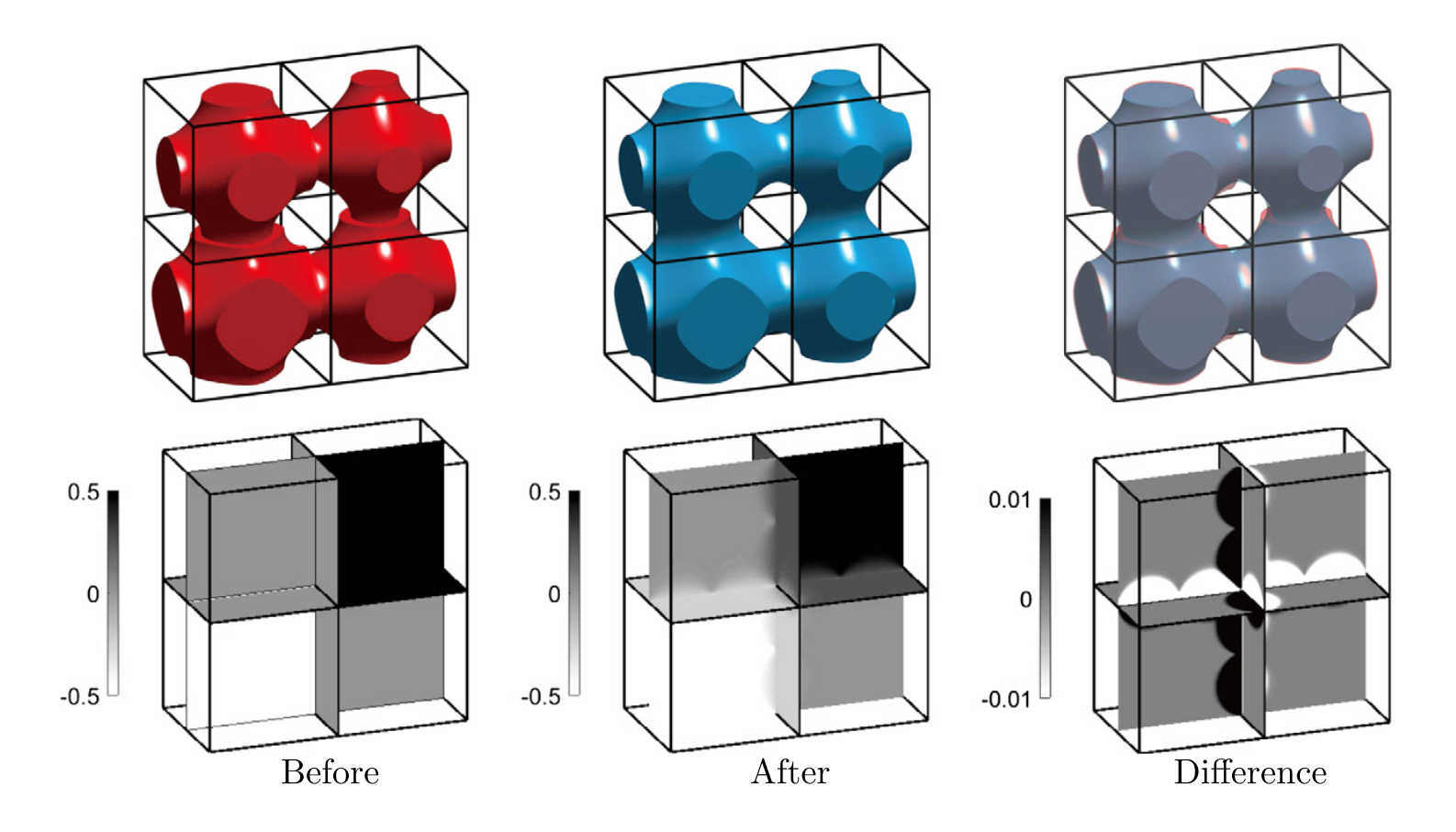
We propose an approach to design an optimized heterogeneous interconnected porous structure over a fixed macro-design mesh for performance optimization, which has seldom been addressed despite its extensive potential industrial applications. We achieve this by introducing the concept of the extended triply periodic minimal surface (ETPMS), defined by an implicit function with additional control parameters that can prescribe the element anisotropy and heterogeneity consistently. The performance of the approach is demonstrated using a suite of three-dimensional benchmark examples.

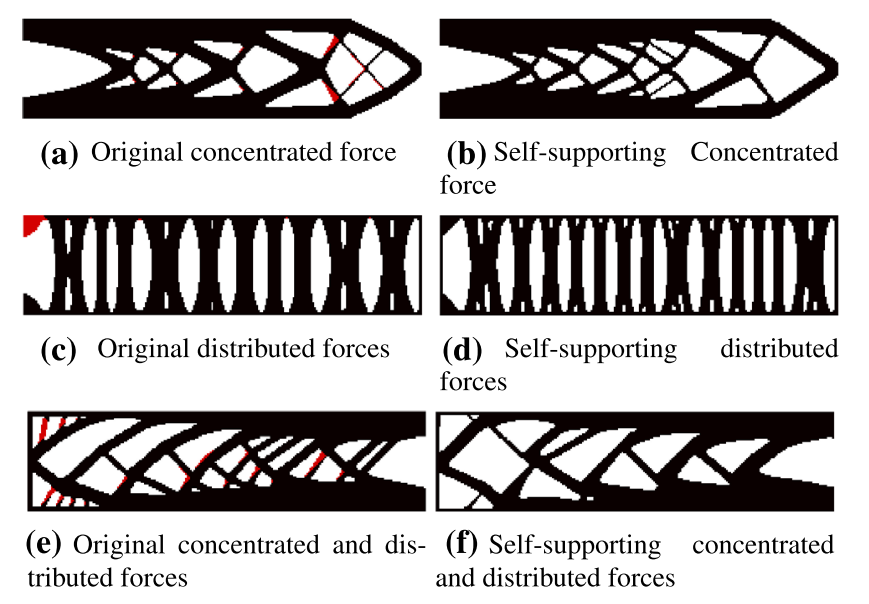
The Visual Computer, 2020
This paper presents an application framework that provides a complete processto design an optimized self-supporting structure, ready to be fabricated via additive manufacturing without the usage of additional support structures. Such supports in general have to be created during the fabricating processso that the primary object can be manufactured layer by layer without collapse; this process is very time-consuming and waste of material. The main approach resolves this issue by formulating the selfsupporting requirements as an explicit quadratic continuous constraint in a topology optimization problem, or specifically, requiring the number of unsupported elements (in terms of the sum of squares of their densities) to be zero.

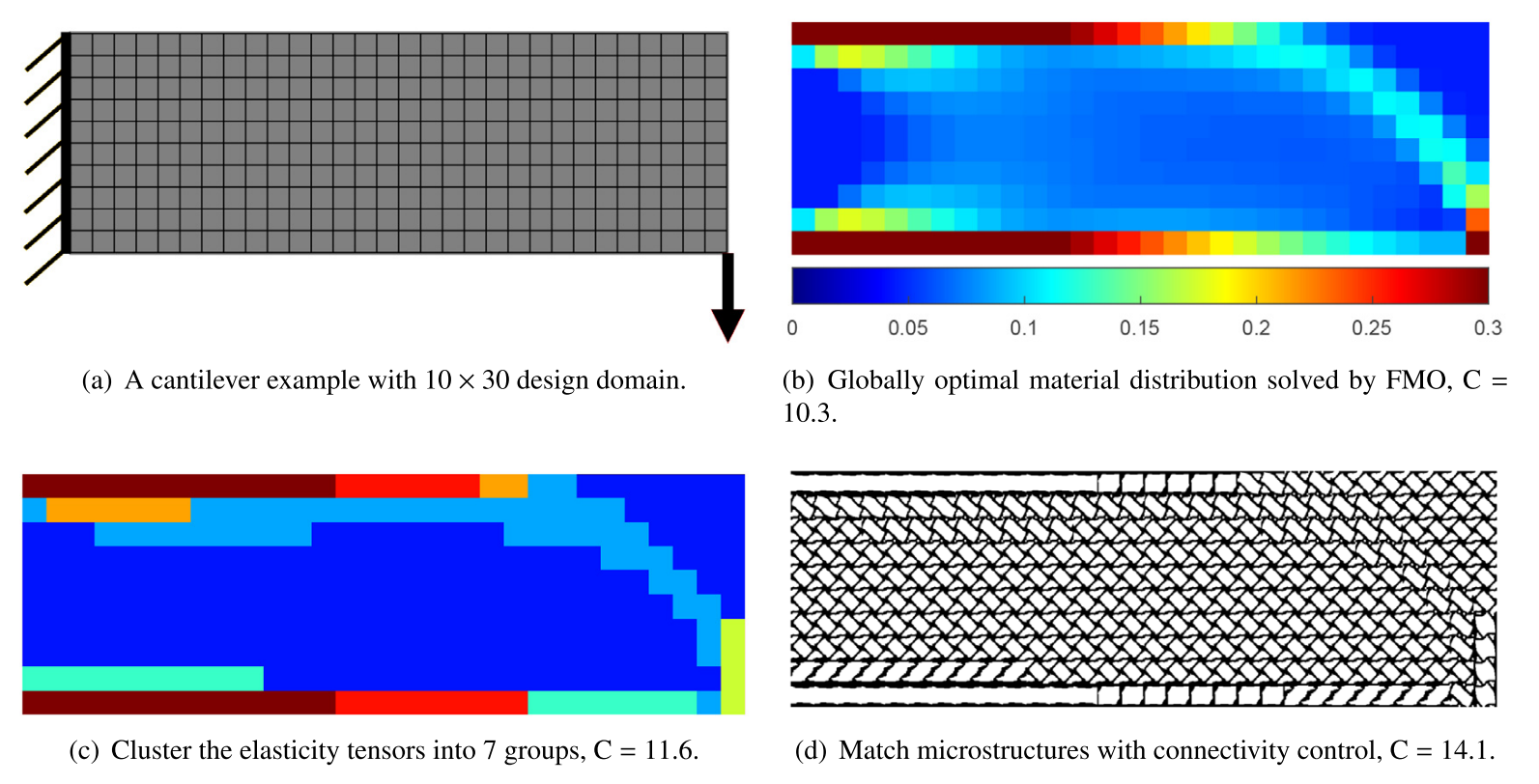
Computer-Aided Design, 2020
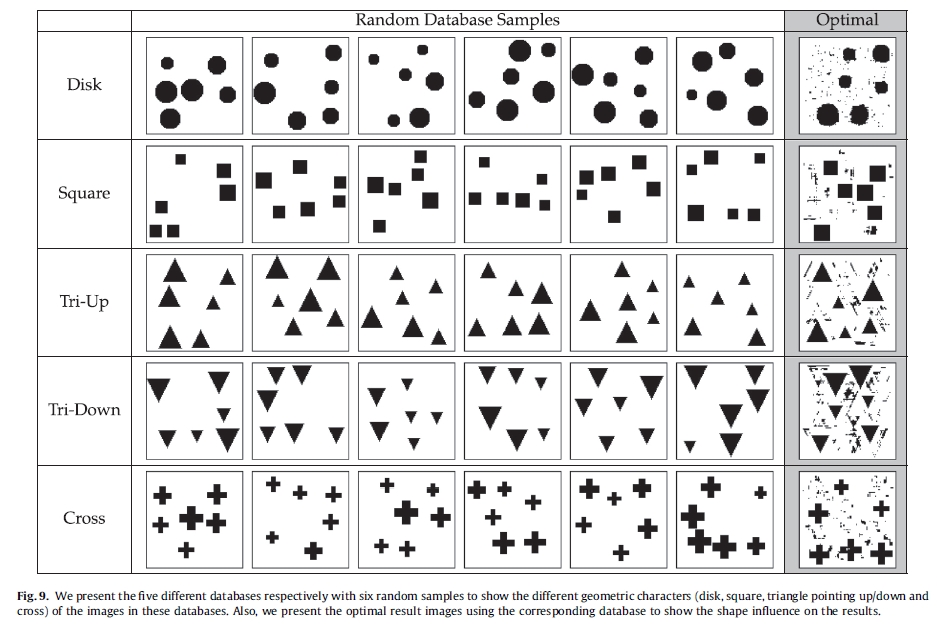
The study aims to find a manufacturable cellular structure of valid geometry under certain volume usage budget, given a fixed design domain under external loadings. It is achieved via first introducing the concept of free material optimization (FMO), which provides an ultimately best structure among all possible elastic continua. After this, two novel control strategies are developed in combination with inverse homogenization to ultimately produce a cellular structure of valid geometric connectivity. It mainly includes approaches of material space reduction via hierarchical clustering, and a novel physics-based connectivity control to tailor the geometric connectivity between neighboring microstructures. ...

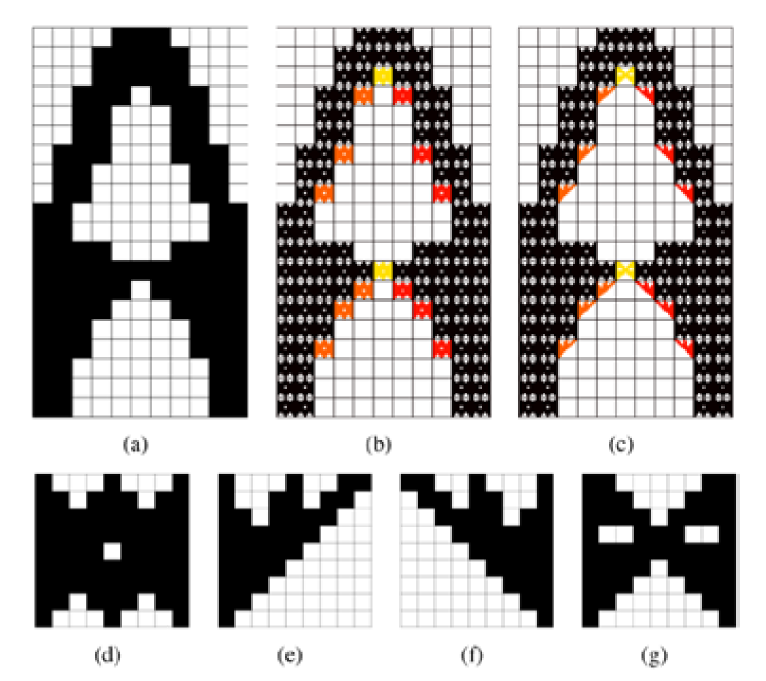
The Visual Computer, 2021; ACDDE Best Paper
Although biscale topology optimization has been widely studied, conducting self-supporting topology optimization separately for the macro-structure and for each micro-structure is not sufficient to produce an overall self-supporting structure, as first observed in this study. The issue is resolved via an approach to bridge the gap between the requirements of self-supporting at the two scales via distinguishing the macro-cells based on their relative locations. Ultimately, a completely self-supporting overall structure is generated within a biscale topology optimization framework and extends its potentiality to produce design to be directly fabricated via additive manufacturing. Performance of the approach is demonstrated via various 2D and 3D examples.

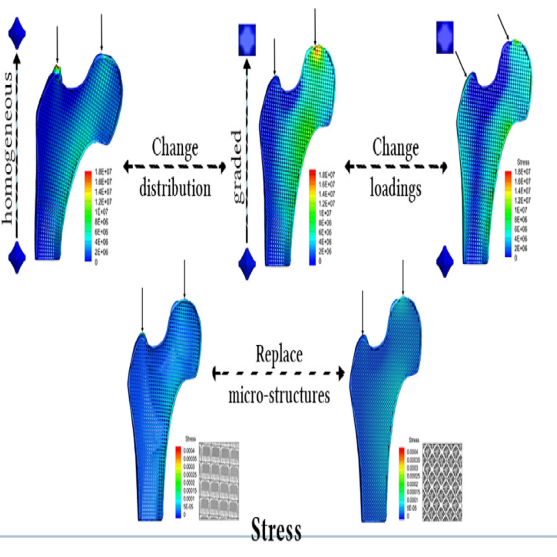
Visual informatis, 2019
This paper aims to instantly predict within any accuracy the stress distribution of cellular structures under parametric design, including the shapes or distributions of the cell geometries, or the magnitudes of external loadings. A classical model reduction technique has to balance the simulation accuracy and interaction speed, and has difficulty achieving this goal. We achieve this by computing offline a design-to-stress mapping that ultimately expresses the stress distribution as an explicit function in terms of its design parameters. The well-known curse of dimensionality intrinsic to the high-dimension problem is (partly) resolved through a spatial separation using two main techniques. Extensive 2D and 3D examples are shown to demonstrate the approach’s performance.

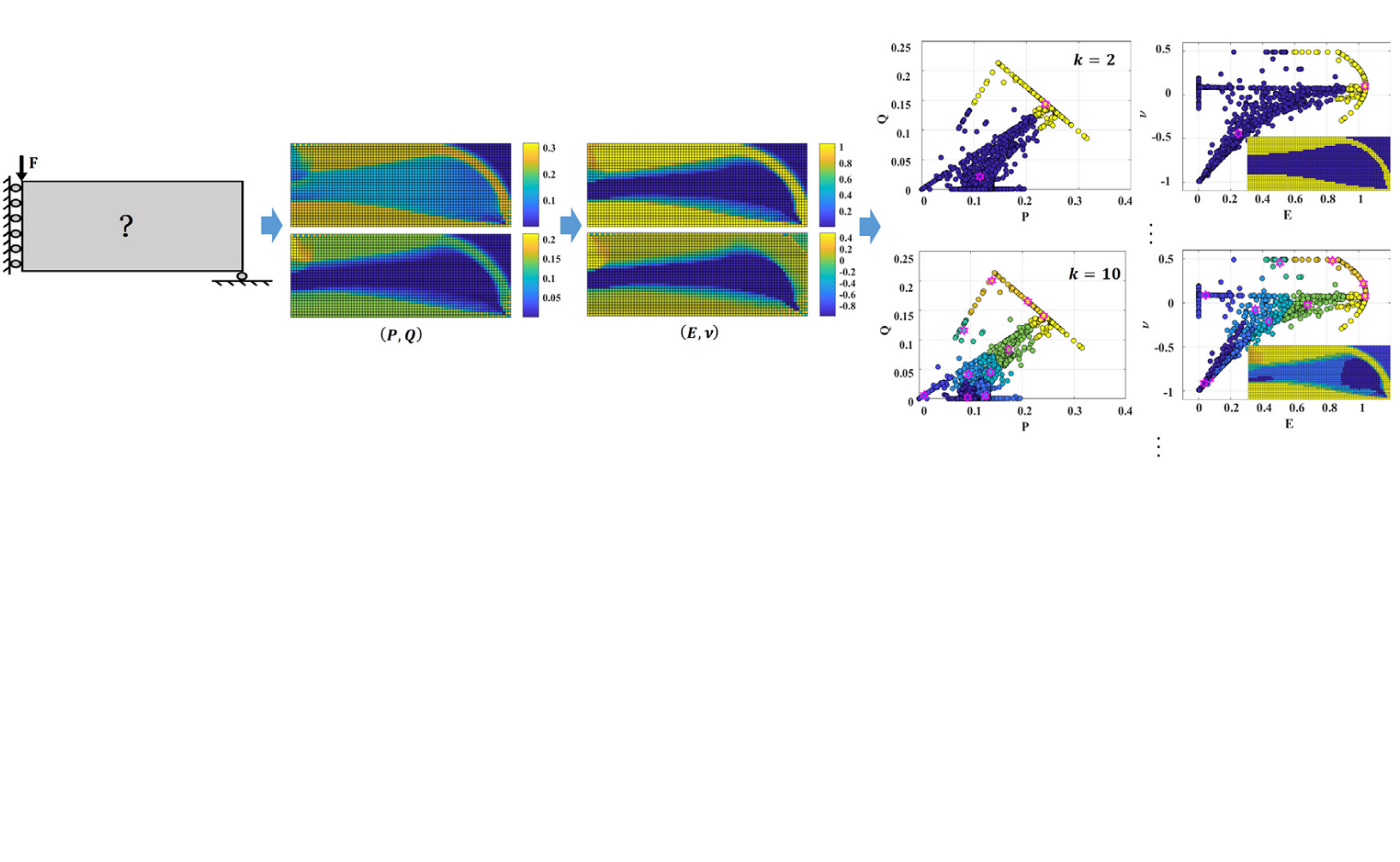
Computer-Aided Design, 2019
The problem of free isotropic material optimization (FIMO) is studied that takes as design variables both Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio at each point of the design domain without constraints on its manufacturability; certain necessary conditions on the material attainability are the only imposed requirements. Global optimum to the FIMO is achieved via rigorously reformulating it as a second order cone programming, to which a global optimum is theoretically verified and numerically trackable; the novel formulation also avoids the challenging singularity issue on void elements. The generated structure can be taken as benchmark solutions with which other optimized designs can be compared, and to propose novel new product design. ...


Computer-Aided Design, 2019
A novel generative design approach is developed in this study, producing a mechanically optimized topological design while simultaneously mimicking an input exemplar texture. The textures are believed embedding certain functional information intrinsic to these objects. Designing objects similar to these textures will not only maintain such functions within the design but also widely expand the design space to explore more design options. Ultimately, we can create a set of design options both physically optimized and geometrically smooth for generative design. Extensive numerical results were also tested to demonstrate the approach’s performance.

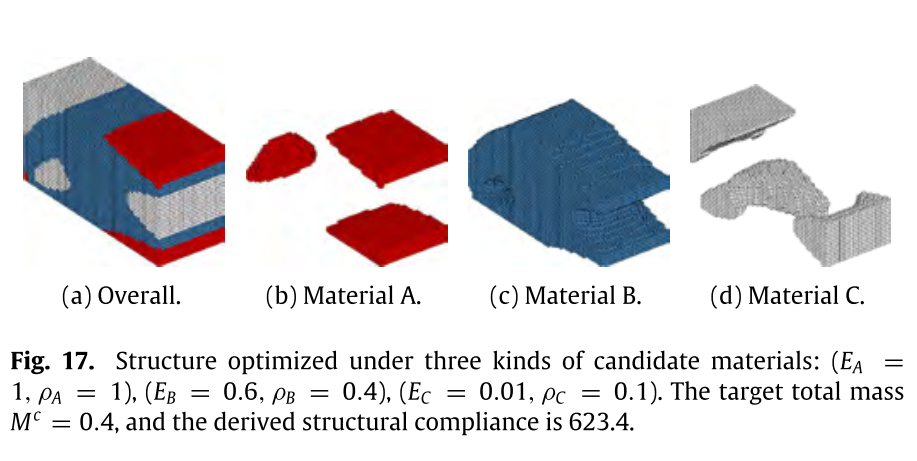
Computer-Aided Design, 2018
A novel approach to computing the discrete solution to the challenging multi-material topology optimization problem under total mass constraint is studied in this paper. The challenge of the problem lies in the incompressibility constraint on the summation of the usage of the total materials, which significantly increases the associated computational difficulty. Solution to the optimization problem is derived on a theoretical finding that the iterative density update in a two-material optimization problem is totally determined by the rankings of the elemental compliances, which only involves an FE analysis computation, and can be efficiently achieved.

[59] Haroon Ijaz, Xuwei Wang, Wei Chen, Hai Lin, Ming Li*. Physically reliable 3D styled shape generation via structure-aware topologyotimization in unified latent space. Computer-Aided Design, 2025.
[58] Jiajie Guo, Ming Li*. Augmented Sphere Tracing for Real-time Editing Mega-scale Periodic Shell-lattice Structures. Computer-Aided Design, 2025.
[57] 李默;蔡晨曙;陈俊诏;王萍;赵博;曾龙;李明;方强. 基于二维图纸的机载线缆三维重建方法. 图学学报, 2025.
[56] 张人杰, 王祯霖, 耿慧, 林郁, 陈俊诏, 李明*, 方强基于通道设计的电气导线互联系统线缆自动布局方法, CAD&CG 学报, 2025.
[55] Feng Yang, Ping Wang, Qiong Zhang, Wei Chen, Ming Li*, Qiang Fang*. A Coarsened-Shell based Cosserat Model for Simulation of Hybrid Cables. Electronics. 2024
[54] Feng Yang, Ping Wang, Renjie Zhang, Shuyu Xing, Zhenlin Wang, Ming Li *,Qiang Fang *. A-ACO Algorithm for Multi-Branch Wire Harness Layout Planning. Electronics. 2024.
[53] Wei Chen; Ming Li; Coarsened C1-continuous shape functions using B-spline patches for simulating nonlinear heterogeneous structures, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 421:116808.
[52] Liangchao Zhu; Xuwei Wang; Weidong Zhong; Ming Li; Learning microstructure–property mapping via label-free 3D convolutional neural network, The Visual Computer, 2024, 40(0):7025-7044.
[51] Ming Li; Jingqiao Hu; Wei Chen; Weipeng Kong; Jin Huang; Explicit Topology Optimization of Voronoi Foams, IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2024, 0(0):1-16.
[50] Ming Li, Yongcun Song, Xingtong Yang, Kai Zhang. Lattice structure design optimization under localized linear buckling constraints. Computers & Structures, 2023.
[49] Jinsan Cheng, Bingwei Zhang, Yikun Xiao, Ming Li. Topology-driven approximation to rational surface-surface intersection via interval algebraic topology analysis. ACM Trans. Graphics (Siggraph) , 2023.
[48] Ming Li, Chengfeng Lin, Wei Chen, Yusheng Liu, Shuming Gao, Qiang Zou*, XVoxel-Based Parametric Design Optimization of Feature Models. Computer Aided Design, 2023.
[47] 李 明, 张乘虎, 扈婧乔, 胡心卓, 刘继凯.多孔模型设计方法. 图学学报,43(6),2022.
[46] Ming Li, Jingqiao Hu. Analysis of heterogeneous structures of non-separated scales using curved bridge nodes, CMAME 2022
[45] Dengyang Zhao&, Ting Ting Gu, Yusheng Liu, Shuming Gao, Ming Li*, Constructing self-supporting structures in biscale topology optimization, the Visual Computer, 2022- 05, 38, 3, 1065-1082
[44] Ming Li, Liangchao Zhu, Jingzhi Li, Kaizhang. Design Optimization of Interconnected Porous Structures Using Extended Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces. Journal of Computational Physics, 2020.
[43] D. Zhao, Ming Li*, Y. Liu. A novel application framework for self-supporting topology optimization. the Visual Computer, 2020.
[42] JQ. Hu, Ming Li* , XT. Yang, SM. Gao. Cellular Structure Design based on Free Material Optimization under Connectivity Control. Computer-Aided Design 127 (2020).
[41] Dengyang Zhao, Ming Li*, Yusheng Liu and Shuming Gao. Building print-ready structures in biscale topology optimization framework. International Congress and Conferences on Computational Design and Engineering, 2019. Best paper.
[40] Liangchao Zhu, Ming Li*, Weiwei Xu, Kun Zhou. Direct Design to Stress Mapping for Cellular Structures. Visual informatis, 2019.
[39] Mengqi Kong, Shuqi Wang, Ming Li etc. A wearable microfluidic device for rapid detection of HIV-1 DNA using recombinase polymerase amplification. Talanta, 205(1), 120155, 2019.
[38] Ming Li, Jingzhi Li, Ralph Martin and Kai Zhang. A Numerical Framework to Simplify CAD Models for Reliable Estimates of Physical Quantities. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech., 11:870-889, 2019.
[37] Xingtong Yang and Ming Li. Free Isotropic Material Optimization via Second order Cone Programming. Computer-Aided Design, 115:52-63, 2019.
[36] Generating Quantitative Product Profile Using Char-Word CNNs Competitiveness Evaluation of Product Design Using Online Customer Reviews. Asian Conference on Digital Design and Engineering, 2018.
[35] Hu J., Li M.*, Gao S . Texture-guided generative structural designs under local control. Computer-Aided Design, 2018.
[34] Qin FW. Xu H. Li. M et al. Voice of the customer oriented new product synthesis over knowledge graph. ASME DETC/CIE, 2018.
[33] Xu C. Li. M. Performance oriented design of semiregular anisotropic porous structures. ASME DETC/CIE, Quebec City, Canada, 2018.
[32] Yang X., Li M.* Discrete multi-material topology optimization under total mass constraint. Computer-Aided Design, 102:182-192, 2018.
[31] Gang Xu, Ming Li, Bernard Mourrain etc. Constructing IGA-suitable planar parameterization from complex CAD boundary by domain partition and global/local optimization. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 328, 2017.
[30] Xu, C., Li, M*., Huang, J.,Gao, S. (2017). Efficient biscale design of semiregular porous structures with desired deformation behavior. Computers & Structures, 182, 284-295, 2017.
[29] Xu C, Gao S, Li M*. A novel PCA-based microstructure descriptor for heterogeneous material desig
n[J]. Computational Materials Science, 130:39-49, 2017.
[28] Zhang K, Li M, Li J. Estimation of Impacts of Removing Arbitrarily Constrained Domain Details to the Analysis of Incompressible Fluid Flows[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2016, 20(4):944-968.
[27] F Qin,S Gao,X Yang,M Li,J Bai. An ontology-based semantic retrieval approach for heterogeneous 3D CAD models[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2016, 30(4):751-768.
[26] L. Zhu, M. Li*, and R. Martin. "Direct simulation for CAD models undergoing parametric modifications." Special Issue of ACM Solid and Physical Modeling (SPM) 2016 in Computer-Aided Design,2016.
[24]. M. Li, Engineering analysis reliable CAD model simplification, Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics (In Chinese). 27(8):1363-1375, 2015.
[23] C.Xu, S.Gao, M Li*. Hetergoeneous material design using a PCA-based microstructure representive method, ASME IDETC/CIE 2015.
[22] M.Li*, B. Zhang, and R. Martin. "Second-order defeaturing error estimation for multiple boundary features." International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 100(5): 321-346 (2015).
-->
[21] M. Li*, S. Gao and K. Zhang. A goal-oriented error estimator for the analysis of simplified designs. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 255: 89 - 103,2013.
[20] M. Li*, S. Gao and R. Martin.Engineering analysis error estimation when removing finite-sized features in nonlinear elliptic problems. Special Issue of ACM Solid and Physical Modeling (SPM) 2012 in Computer-Aided Design 45(2):361-372,2013.
[19] M. Li*, J. Zheng and R. Martin. Quantitative control of idealized analysis models of thin designs. Computers & Structures, 106-107:144-153, 2012.
[18] J. Tang, S. Gao* and M. Li. Evaluating defeaturing-induced impact on model's analysis.Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2012.
[17] Y. Liu, C. Xian, M. Li, H. Xia and S. Gao. A local adaptation-based generation method of medial axis for efficient engineering analysis.Engineering with Computers, 2012.
[16] H Zhu, S Gao*, M. Li and W. Pan. Adaptive Tetrahedral remeshing for modified solid models.Graphical Models, 74(4):76-86, 2012.
[15] M. Li, S. Gao* and R. Martin.Estimating the effects of removing negative features on engineering analysis. Special Issue of ACM Solid and Physical Modeling (SPM) 2011 in Computer-Aided Design 43(11): 1402–1412, 2011.
[14] M. Li* and S. Gao.Estimating defeaturing-induced engineering analysis error for arbitrary 3D features.Computer-Aided Design 43(12): 1587–1597, 2011.
[13] W. Pan, S. Gao*, H. Zhu, M. Li and J. Chen. Identifying different entities for minor model modification based on common primary subpart. Computer-Aided Design & Applications 8(3): 345-356, 2011.
[12] H. Wu, S. Gao, Y. Cao, M Li* and Y Liu.Rapid generation of feature-based multi-resolution FEM model.Proceedings of ACDDE 2010.
[11] H. Zhu, S. Gao and M. Li. Adaptive Remeshing for modified solid model through mesh re-use. Proceedings of ACDDE 2010.
[10] M. Li, F. Langbein and R. Martin. Detecting design intent in approximate CAD models using symmetry. Computer-Aided Design 42 (3), 183-201, 2010.
[9] Ming Li, FC Langbein, RR Martin. Detecting approximate symmetry of discrete point subsets, Computer-Aided Design, 40(1):76-93, 2008.
[8] Ming Li, FC Langbein, RR Martin. Detecting approximate incomplete symmetries in discrete point sets.Proc. ACM Solid and Physical Modeling, 335-340, 2007.
[7] Ming Li, Xiao-Shan Gao, ShangChin Chou. Rational quadratic approximation to plane parametric curves and its applications in approximate implicitization, The Visual Computer, 22(9-11):906-917, 2006.
[6] Ming Li, F. Langbein, R. Martin, Constructing regularity feature trees for solid models, Proc. IEEE Geometric Modeling and Processing, LNCS 4077, 2006.
[5] Jin-Shan Cheng, Xiao-Shan Gao, Ming Li. Determining the Topology of Real Algebraic Surfaces, Mathematics of Surfaces XI, R. Martin, H. Bez, M. Sabin (editors), LNCS 3604, Springer-Verlag, 2005, pp. 121-146.
[4] Ming Li, Xiao-Shan Gao, and Jin-Shan Cheng. Generating Symbolic Interpolants for Scattered Data with Normal Vectors, Journal of Computer Science and Technology, Nov. 2005, Vol. 20, No.6, 861-874.
[3] Xiao-Shan Gao, Ming Li. Rational quadratic approximation to real algebraic curves, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 21(8):805-828, 2004. (SCI)
[2] Xiao-Shan Gao, Ming Li, Rational quadratic approximation to real plane algebraic curves Proc. IEEE Geometric Modeling and Processing, 93-102, 2004.
[1] Xiao-Shan Gao, Ming Li, Construct piecewise Hermite interpolation surface with blending methods, Proc. IEEE Geometric Modeling and Processing, 53-59, 2002.