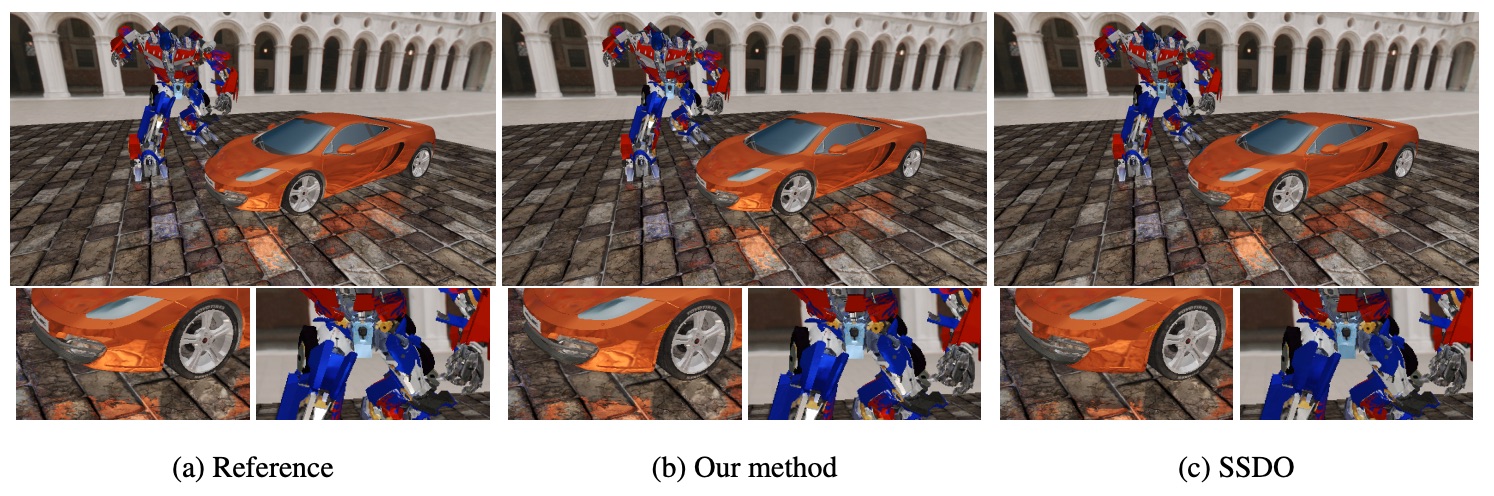
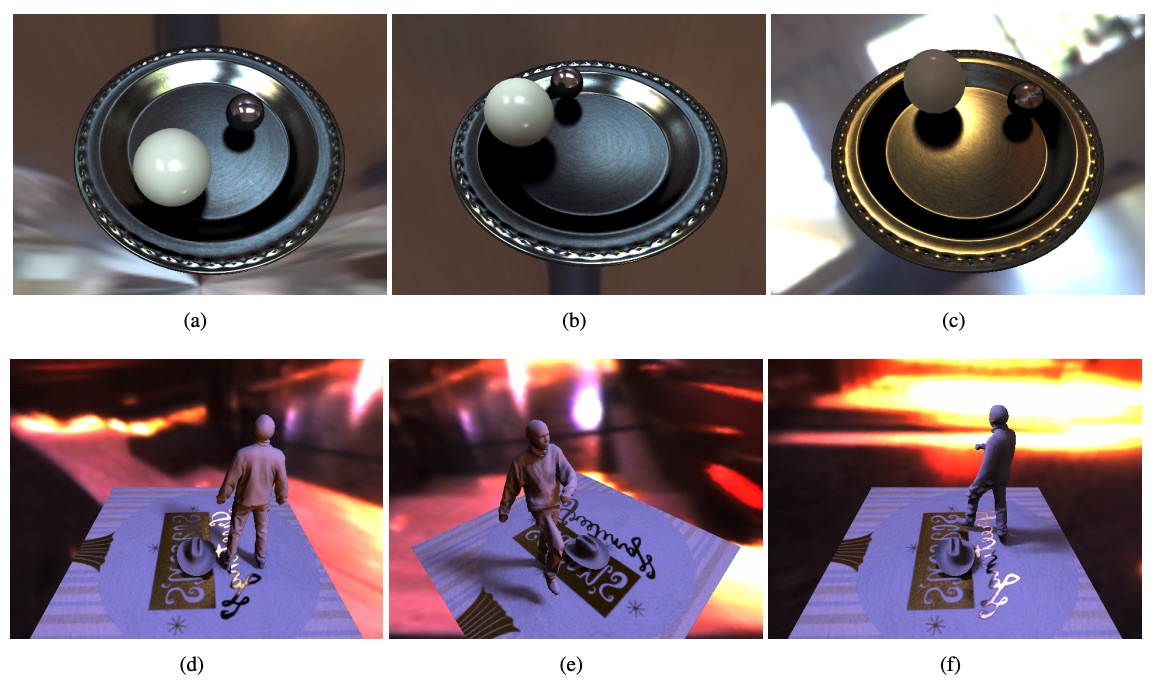
Parallel and Adaptive Visibility Sampling for Rendering Dynamic Scenes with Spatially-Varying Reflectance
Rui Wang,
Minghao Pan, Xiang Han, Weifeng Chen,
Hujun Bao
State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University
CAD/GRAPHICS 2013, Computers & Graphics, vol.38, pp. 374-381, February 2014.