EyelashNet: A Dataset and A Baseline Method for Eyelash Matting
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. of Siggraph Asia'2021), 2021, 40(6): Article 217.
Qinjie Xiao, Hanyuan Zhang, Zhaorui Zhang, Yiqian Wu, Luyuan Wang, Xiaogang Jin, Xinwei Jiang, Yongliang Yang, Tianjia Shao, Kun Zhou
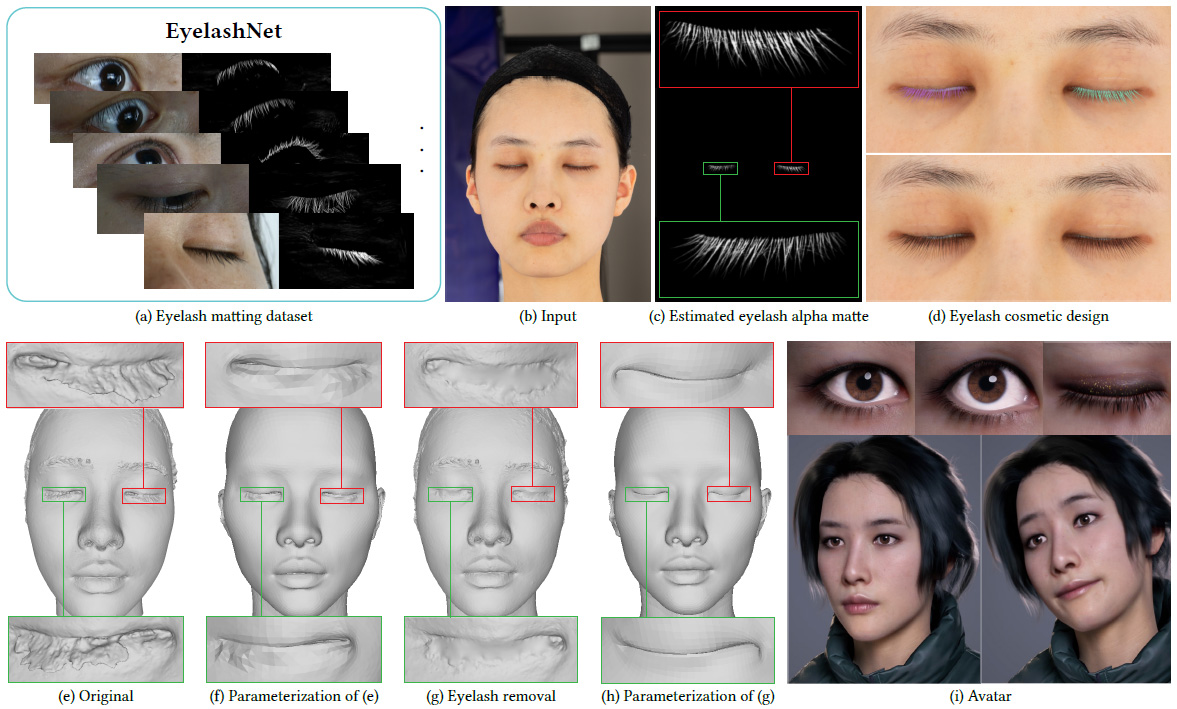
We create EyelashNet, the first eyelash matting dataset (a). This allows training a deep matting network that can automatically estimate high-quality eyelash alpha mattes (c) from an input portrait (b), where the alpha matte of the left/right eye is shown in the green/red box. In a high-fidelity avatar reconstruction pipeline, the eyelash alpha matting enables us to remove the interference of eyelashes during the multi-view stereo (MVS) based 3D face reconstruction process, and therefore largely enhances the efficacy and efficiency of the reconstruction of eye regions. Without eyelash removal, the reconstructed eyelash geometry (e) often induces noises and artifacts when fitting the eyelid during 3D parametric face reconstruction (f), which requires very expensive manual repair in hours. In contrast, eyelash matting helps to easily achieve a better geometry of the eye region (g). As a result, more faithful eyelids with much higher quality can be reconstructed. We show the fully rigged avatar in (i) for completeness. In addition, our eyelash alpha matting method can be applied for cosmetic design such as eyelash recoloring (d, top) and eyelash editing (e.g, lengthening the eyelashes) (d, bottom).
Abstract
Eyelashes play a
crucial part in the human facial structure and largely affect the facial
attractiveness in modern cosmetic design. However, the appearance and
structure of eyelashes can easily induce severe artifacts in high-fidelity
multi-view 3D face reconstruction. Unfortunately it is highly challenging to
remove eyelashes from portrait images using both traditional and learning
based matting methods due to the delicate nature of eyelashes and the lack
of eyelash matting dataset. To this end, we present EyelashNet, the first
eyelash matting dataset which contains 5,400 high-quality eyelash matting
data captured from real world and 5,272 virtual eyelash matting data created
by rendering avatars. Our work consists of a capture stage and an inference
stage to automatically capture and annotate eyelashes instead of tedious
manual efforts. The capture is based on a specifically-designed fluorescent
labeling system. By coloring the eyelashes with a safe and invisible
fluorescent substance, our system takes paired photos with colored and
normal eyelashes by turning the equipped ultraviolet (UVA) flashlight on and
off. We further correct the alignment between each pair of photos and use a
trained matting network to extract the eyelash alpha matte. As there is no
prior eyelash dataset, we propose a progressive training strategy that
progressively fuses captured eyelash data with virtual eyelash data to learn
the latent semantics of real eyelashes. As a result, our method can
accurately extract eyelash alpha mattes from fuzzy and self-shadow regions
such as pupils, which is almost impossible by manual annotations. To
validate the advantage of EyelashNet, we present a baseline method based on
deep learning that achieves state-of-the-art eyelash matting performance
with RGB portrait images as input. We also demonstrate that our work can
largely benefit important real applications including high-fidelity
personalized avatar and cosmetic design.
Download
| PDF, 52.2MB | Video, 88.7MB | Datasets and Source codes |
Acknowledgments: The authors would like to thank Sammi (Xia Lin), Eric (Ma Bingbing), Eason (Yang Xiajun), and Rambokou (Kou Qilong) from Tencent Institute of Games for contributing useful data and relevant application demonstration assistance during the paper's preparation, which provided significant support for the paper's completion.